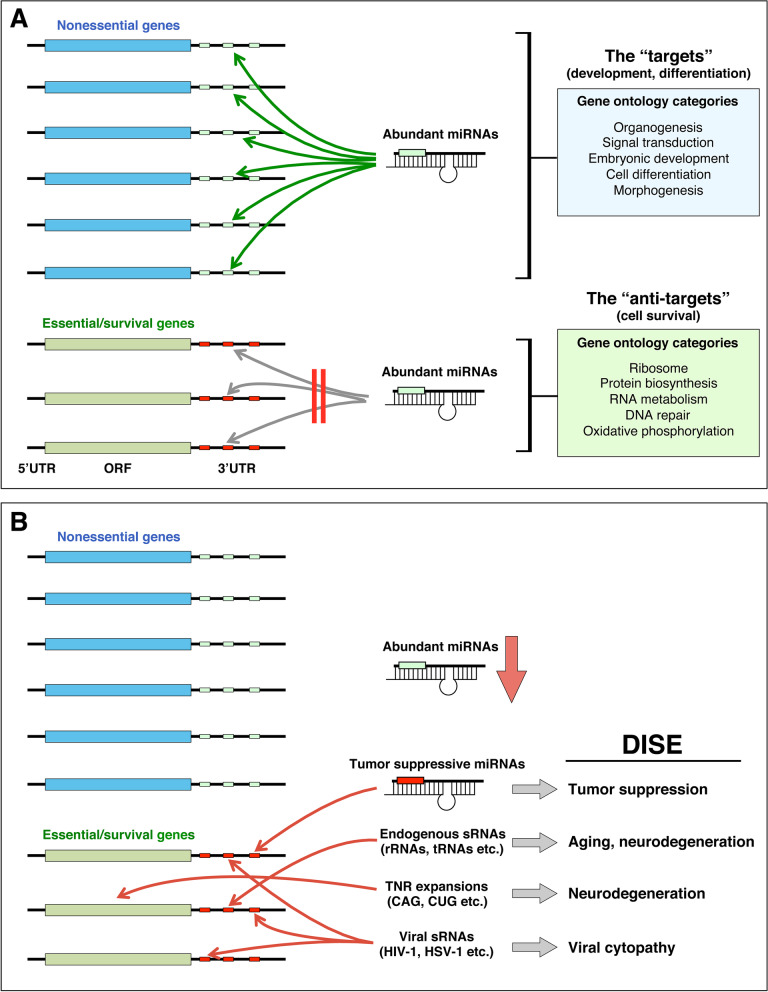
Fig. 1.
Model to illustrate the role of DISE/6mer seed toxicity in cancer and other diseases. A High expression of miRNAs with nontoxic seeds. Left: The genome contains ~ 20,000 genes (blue and green genes) of which about ~ 10% are essential for the survival of all cells (green genes), as determined by various lethality screens. Almost all genes contain 3′ UTRs, the predominant location of seed matches targeted by miRNAs. The most abundant miRNAs target seed matches in the 3′ UTR of nonessential genes (light green boxes). Consistently, genes containing seed matches for these highly abundant miRNAs (the ‘targets”), function in biological processes such as development and differentiation (top right) [36]. If such highly abundant miRNAs were to target seed matches in the 3′ UTR of essential survival genes (red boxes), that would result in the death of the cell (bottom left). Consistent with this model, genes devoid of seed matches of highly abundant miRNAs (the “anti-targets”) fall into gene ontology terms that are consistent with cell survival, including protein biosynthesis, DNA repair, and DNA metabolism (bottom right) [36]. B Low expression of miRNAs with nontoxic seeds. Under conditions in which the most abundant miRNAs with nontoxic seeds are lost, specialized miRNAs with G-rich toxic seeds (e.g., miR-34a-5p), which are often tumor suppressive, target C-rich seed matches (red boxes) in the 3′ UTR of essential survival genes (green genes), inducing DISE. When the expression of protective nontoxic miRNAs is reduced sRNAs other than miRNAs can enter the RISC and depending on the type of sRNA and the tissue, this loading of sRNAs could result in degeneration through DISE induction (bottom right). These could be rRNA or tRNA fragments which have been shown to be upregulated in AD [37–39] and aging [40], TNR based sRNAs as shown in multiple diseases including HD, or even sRNAs from pathogens such as viruses. UTR, untranslated region; ORF, open reading frame; DISE, death induced by survival gene elimination; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA; TNR, trinucleotide repeat