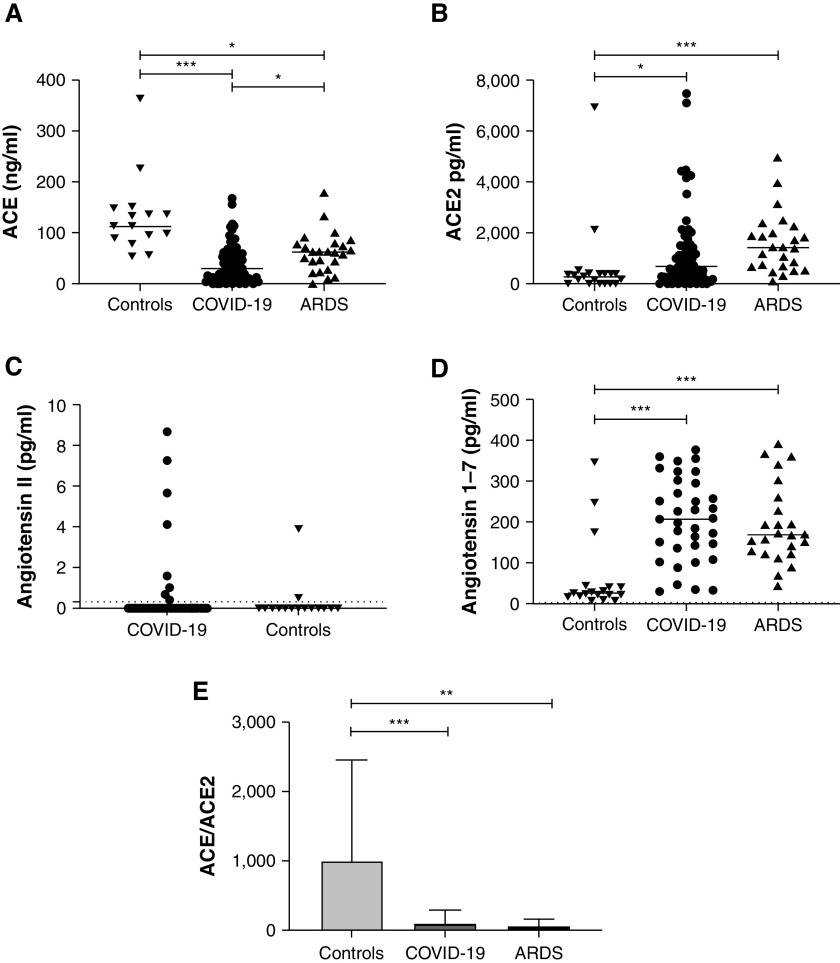
Figure 3.
Quantification of ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme), ACE2, angiotensin II (Ang II), and Ang (1–7) serum concentrations and of the relative expression of ACE to ACE2 in patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19)–unrelated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), patients with severe COVID-19, and control subjects. (A and B) Serum concentrations of ACE (A) and ACE2 (B) were determined using ELISA in control patients (n = 18), patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 82), and patients with COVID-19–unrelated ARDS (n = 24). (C) Serum concentrations of Ang II were compared using enzyme immunoassay in control patients (n = 18) and those with severe COVID-19 (n = 35). Most values were below the detection threshold (0.3 pg/ml according to manufacturer’s instructions). (D) Serum concentrations of Ang (1–7) were compared using ELISA in control patients (n = 18), patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 35), and patients with ARDS (n = 24). Because of sample availability, Ang (1–7) and Ang II could be quantified in only 35/82 patients with severe COVID-19, and no quantification of Ang II could be made in COVID-19–unrelated ARDS. (E) ACE/ACE2 ratio was calculated as the ratio of the concentrations of ACE and ACE2 (means ± SD). Each dataset was compared separately using Kruskall-Wallis test with a Dunn’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, and ***P < 0.0005.