Figure 3. IL-17 induces Nox1, Duox2 and Duoxa2 expression and generation of hydrogen peroxide during C. rodentium infection.
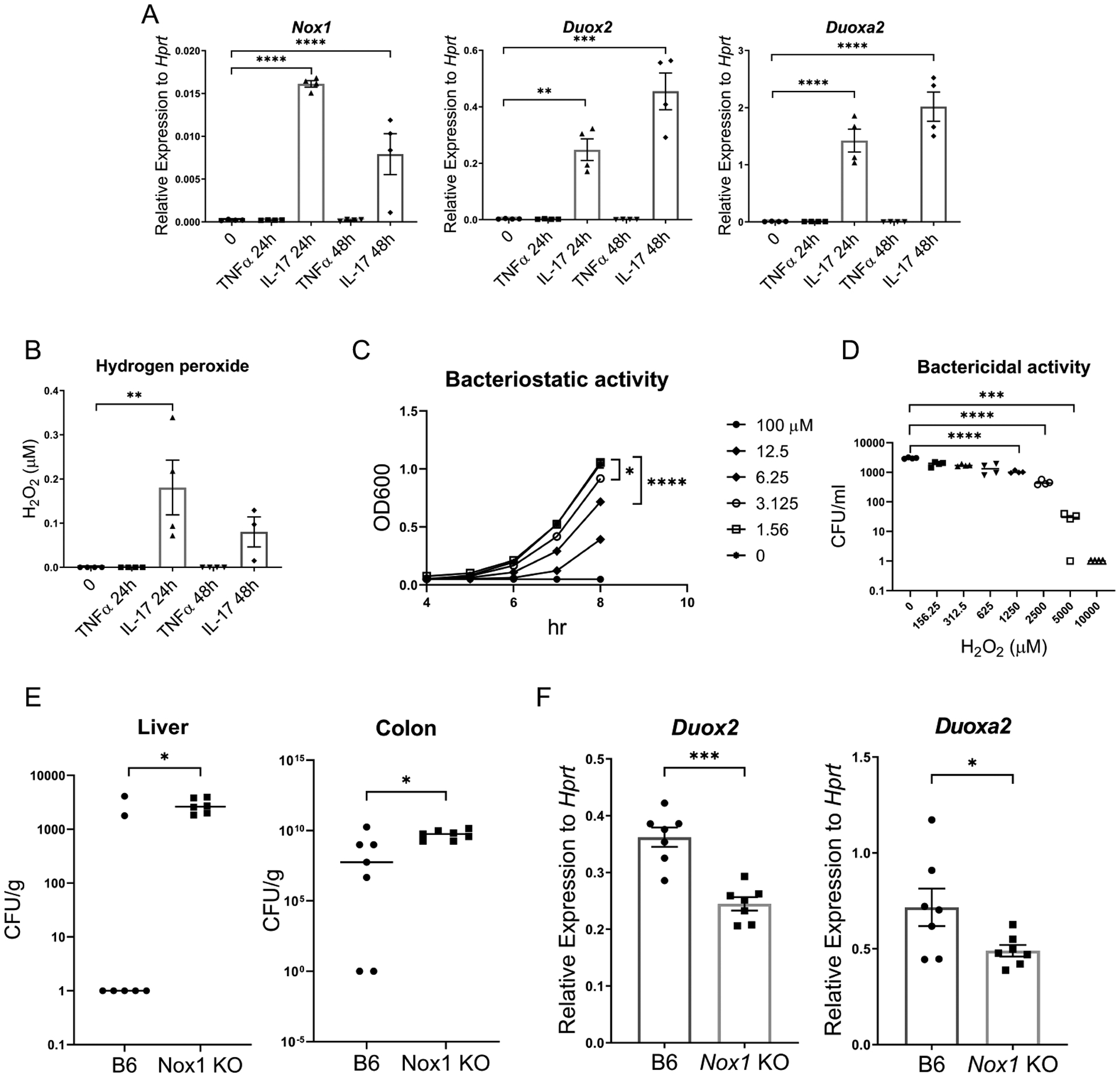
(A) Gene expression of Nox1, Duox2, and Duoxa2, in primary mouse colonic epithelial cell monolayers as measured by RT-PCR after stimulation IL-17A (100 ng/ml) and TNFα (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time. (n=4) (B) Apical hydrogen peroxide production from primary mouse epithelial cell monolayers as measured by the Amplex Red assay. The monolayer was stimulated by IL-17A (100 ng/ml) and TNFα (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time. (C) Bacteriostatic activity of hydrogen peroxide on C. rodentium growth. (D) Bactericidal activity of hydrogen peroxide on C. rodentium (E) C. rodentium burden at day 7 post-infection in Nox1 KO mice and B6 control mice (n=8 per group) (F) Gene expression of Duox2 and Duoxa2 expression in colon tissue measured by RT-PCR. Significant differences are designated by using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (A-D). Significant differences are designated by 2-tailed Mann Whitney test (E) or 2-tailed Student’s t test (F). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Values are means ± SEM.
