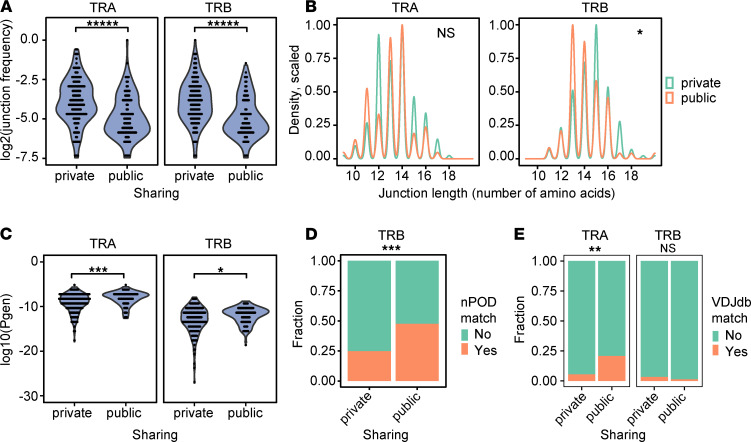
Figure 3. Public and private TCRs have different properties.
(A) Frequency of private junctions was higher than public junctions. Frequencies of public (n = 270) and private (n = 1130) junctions (Supplemental Table 3, public/private TCRs) were compared. Public and private TRA or TRB junctions were combined, and the percentage of junctions in each class was calculated. Violin plots show the probability density of all data without summary statistics. The significance of differences between groups was determined using a 2-sided unpaired Wilcoxon’s signed rank test. *****, FDR < 1 × 10–5. (B) Private TRB junctions were longer than public junctions. Shown are the distributions of amino acid sequence lengths for all unique public and private TRA and TRB junctions (Supplemental Table 3, public/private TCRs) (n = 237 and 227 unique junctions for TRA and TRB chains, respectively). *, FDR < 0.05; NS, not significant. (C) Public TRA and TRB junctions were more germline like than private TRA chains. Shown are V(D)J generation probability values (pgen) for public (n = 270) and private (n = 1130) junctions (Supplemental Table 3, public/private TCRs), calculated using IGoR (50) software. Higher (less negative) pgen values indicate more germline-like V(D)J recombination compared to lower values. The significance of pgen differences between groups was determined using Wilcoxon’s signed rank tests. ***, FDR < 1 × 10–3; *, FDR < 0.05. (D) Public TRB chains show a higher fraction of TRB matches with sequences from pancreatic organ donors. Unique public and private TRB junctions (n = 78 and 149, respectively) (Supplemental Table 3, public/private TCRs) were tested for overlap with nPOD TRB junction sequences from spleen and lymph node (n = 2322 unique junctions). The significance of differences in frequencies of junction matches of public TRB chains with nPOD sequences was assessed by Fisher’s exact test. ***, P < 1 × 10–3. (E) Public TRA junctions show more perfect matches than private junctions with VDJdb junctions. Shown are the fractions of unique public and private TRA and TRB junctions (Supplemental Table 3, public/private TCRs) (n = 237 and 227 unique junctions for TRA and TRB chains, respectively) that overlap with VDJdb junctions (n = 47,069 unique junctions). 15/72 unique public TRA junctions had perfect matches with VDJdb sequences versus 9/165 public TRA junctions. **, FDR < 1 × 10–2.