Figure 2.
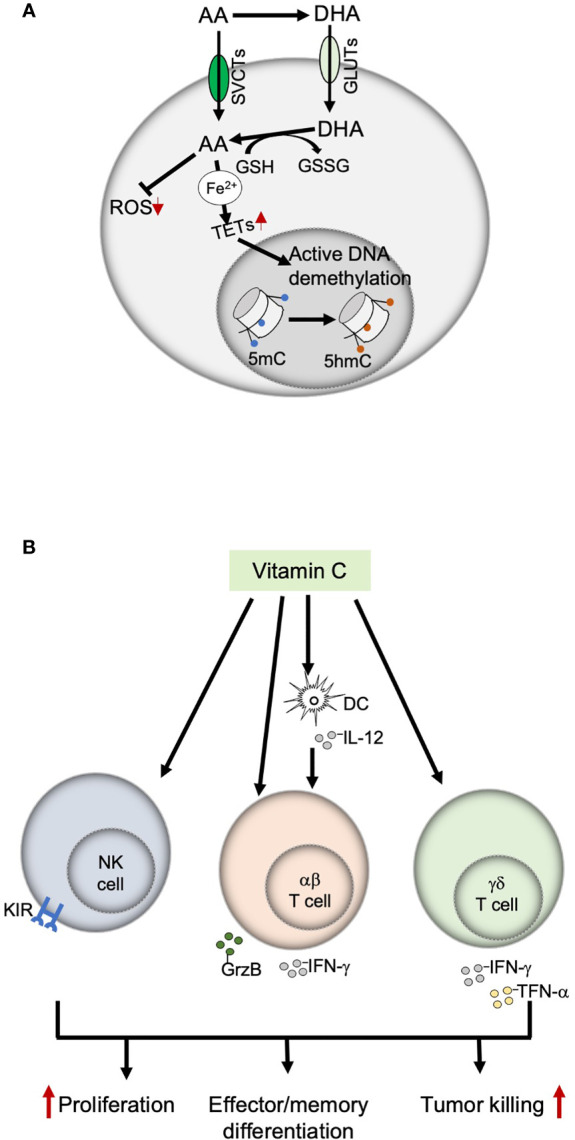
Immunomodulatory functions of Vitamin C. (A) Mechanisms of action of Vitamin C; VitC exerts an immune-modulatory effect on immune cells through two main mechanisms, antioxidant activity and epigenetic modulation (by providing ferrous iron to the TET enzymes, which maintains them in their fully catalytic form, thereby ensuring an active DNA demethylation). (B) Effects of Vitamin C on immune cells with anti-tumor functions. VitC exerts both direct and indirect effects on NK, αβ and γδ T cells by modulating their proliferation, differentiation, and effector functions. AA, ascorbic acid; DHA, dehydroascorbic acid; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide: SVCTs, sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters: GLUTs, glucose transporters: TETs, ten-eleven translocation enzymes; ROS, reactive oxygen species; 5mC, 5-methylcytosine; 5hmC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine.
