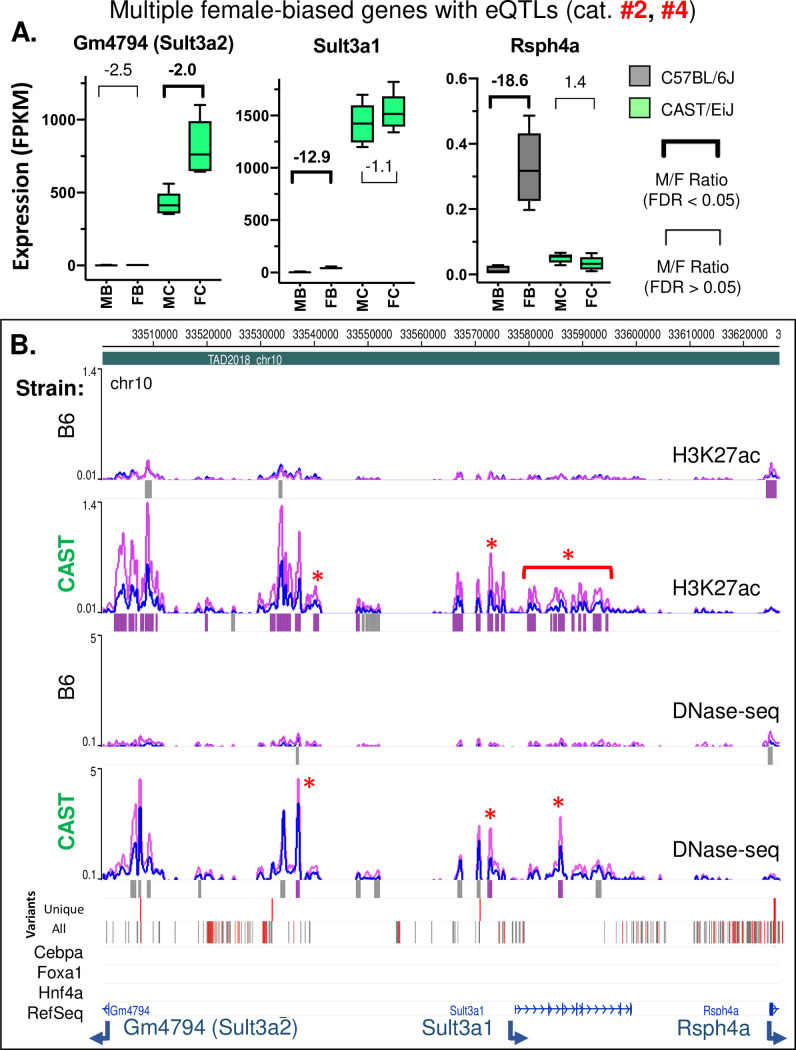
Fig 8. Overlapping eQTLs with different modalities leads to reduction or loss of female bias by different mechanisms.
A. Expression of the female-biased genes Gm4794/Sult3a2 and Sult3a1 is strongly increased in CAST liver, with a stronger genetic effect in males (see regression coefficients, S13A and S13B Fig). This reduces the magnitude of the female bias in expression (category #2 eQTL). The male-biased gene Rsph4a is repressed in female CAST liver, resulting in a loss of female-biased expression (significant only in DO female, category #4 eQTL; see S13C Fig). Data presented as in Fig 5. B. Browser screenshot showing strong increase in CRE activity in CAST compared to B6 liver, with multiple CAST-specific female-biased CREs, and a single female-biased CRE unique to B6 at the promoter of Rsph4a. Horizontal bars beneath the CAST Variants track: grey, single strain-specific variants; red, multiple variants. Data presented as in Fig 5. Additional zoomed in screenshots for Sult3a1 and Rsph4a regions are shown in S13D and S13E Fig.