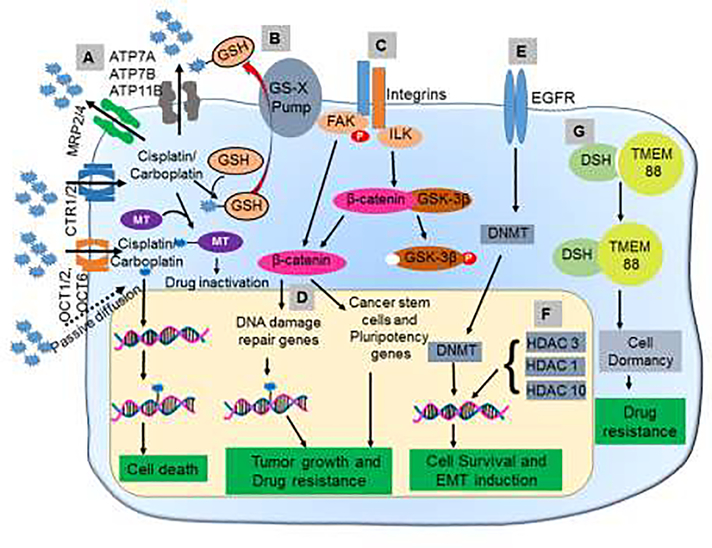
Figure 1. Mechanisms underlying platinum resistance in ovarian cancer.
(A) Dysregulation of transporters associated with cisplatin/carboplatin leads to the reduced influx and increased efflux. (B) GSH and metallothionein mediate the inactivation of platinum compounds via the formation of drug conjugates. (C) Interaction between integrin and ECM promotes platinum resistance by inducing DNA damage repair proteins and CSC genes. (D) Upregulation of DNA damage repair proteins such as BRCA1 enables cancer cells to repair the DNA damage induced by platinum-based drugs and become resistant. (E) The upregulation of EGFR enhances the activity of DNMTs and leads to global methylation and downregulation of proteins regulating proliferation, migration, and invasion. (F) HDACs downregulate genes responsible for apoptosis and proliferation. (G) Inhibition of Wnt signaling mediated through the binding of Dishevelled to TMEM88 leads to cell dormancy and thus resists the action of the cytotoxic drugs. MT=Metallothionein; DSH=Dishevelled; FAK=focal adhesion kinase; ILK=Integrin-linked kinase; OCT=organic cation transporter; GSH=Glutathione; GS-X=Glutathione conjugate export pump; GSK= Glycogen synthase kinase 3; DNMT= DNA Methyltransferase; HDAC=Histone deacetylases; TMEM=Transmembrane Protein 88; EGFR=Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor