Fig. 3.
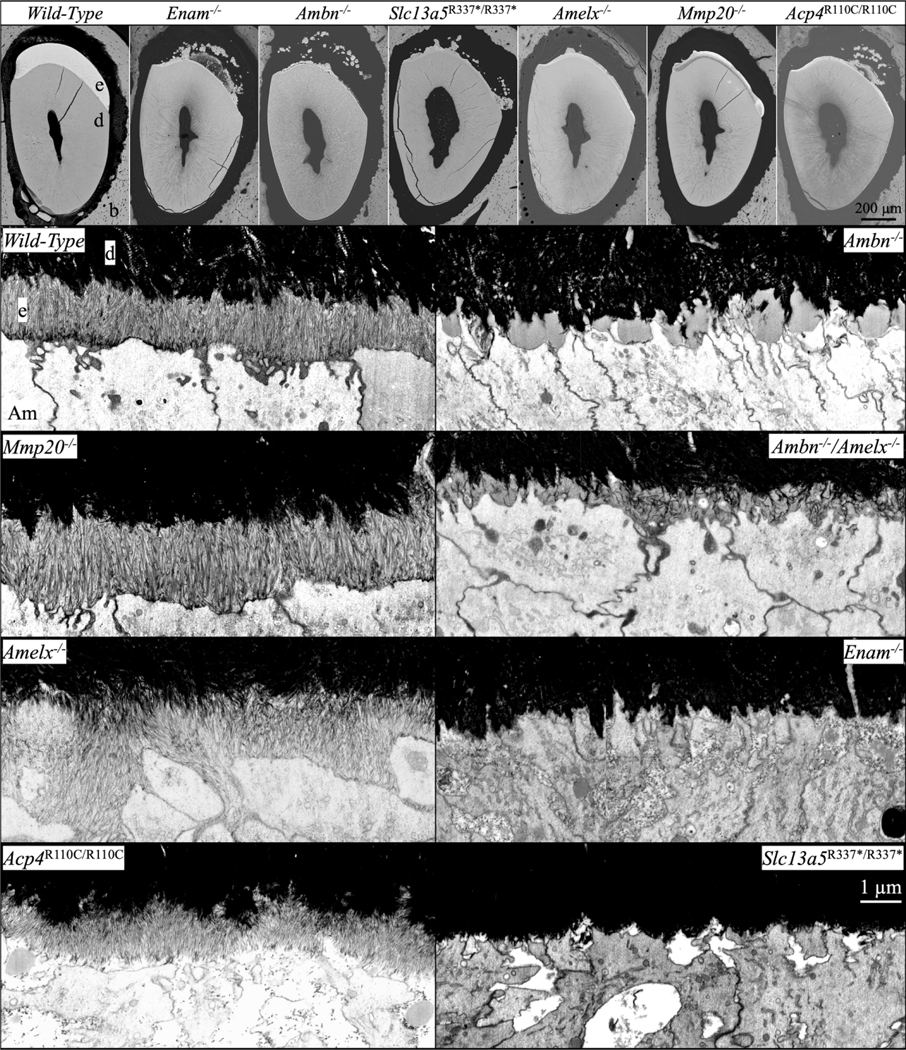
bSEM and FIB-bSEM visualization of initial enamel forming in 7-week mouse mandibular incisors in Amelx−/−, Enam−/−, Ambn−/−, Amelx−/−Ambn−/−, Mmp20−/−, Acp4R110C/R110C, and Slc13a5R337*/R337* mice. Top: bSEM sections of incisor cross-sections at the level of the labial alveolar crest (near the point of eruption). All of the knockouts showed severe enamel hypoplasia, many with ectopic mineral deposition within the overlying enamel organ. Below: FIB-bSEM images of where enamel should be forming in 8 different mouse incisors all at the same magnification. Characteristic initial enamel mineral ribbons form in Mmp20/-, Amelx−/−, and Acp4R110C/R110C mice, while no enamel ribbons form in Enam−/− and Ambn−/− mice. Ambn−/− nulls show accumulations of organic material comprised mainly of amelogenin that are greatly reduced in the Amelx−/−Ambn−/− double null. Key: Am, ameloblast; b, bone; d, dentin; e, enamel.
