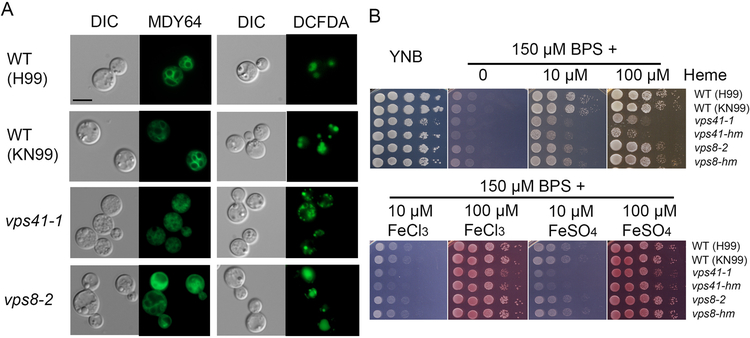
Figure 4. Other candidate CORVET and HOPS complex components influence vacuolar morphology and growth on heme and inorganic iron sources.
(A) Analysis of vacuolar morphology of the WT (both H99 and KN99 background strains) and the deletion strains lacking VPS41 or VPS8 by differential interference microscopy and fluorescent microscopy. The vps41–1 and vps8–2 mutants were constructed in the H99 background for this study, and the vps41-mh vps8-mh were derived from the KN99 strain background (Liu et al., 2008). Cells were harvested from the overnight cultures in minimum medium (MM) and vacuoles were stained with MDY-64 or c-DCFDA. Representative mutants are shown. Bar = 5 μm. (B) The growth of vps41 and vps8 mutants and the WT strain was tested on yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD), yeast nitrogen base (YNB) and YNB plus BPS supplemented with either heme at 10 μM or 100 μM at pH 7.0, or with FeCl3 or FeSO4 at 10 μM or 100 μM at pH 7.0. For all spot assays, tenfold serial dilutions of each strain (labeled on the right) were spotted on the indicated media after iron starvation and the plates were incubated at 30 °C for 2 days before being photographed.