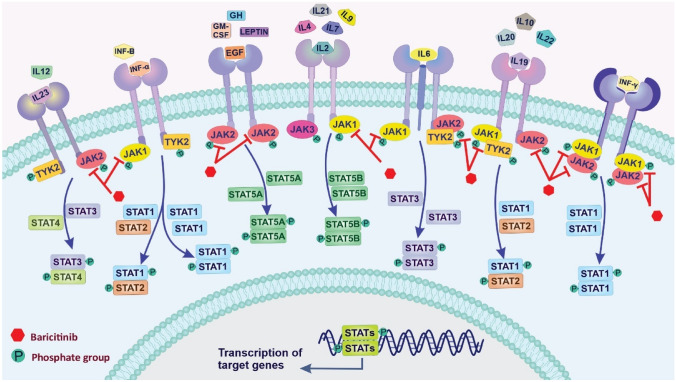
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and inhibition effects of baricitinib. Various cytokines and growth factors can participate in signal transmission through the JAK pathway, including different interleukins (ILs), interferons (INFs α, β, and γ), granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), growth hormone (GH), epidermal growth factor (EGF), and leptin hormone. Interaction between the receptors and ligands leads to phosphorylation of the tyrosine residues of many target proteins by JAK enzymes and affects signal translocation from the extracellular to the intracellular. Then, phosphorylated STATs form dimers (STAT-STAT) can translocate into the nucleus, bind to specific DNA sequences, and transmit extracellular cytokine signals into transcriptional responses