FIGURE 5.
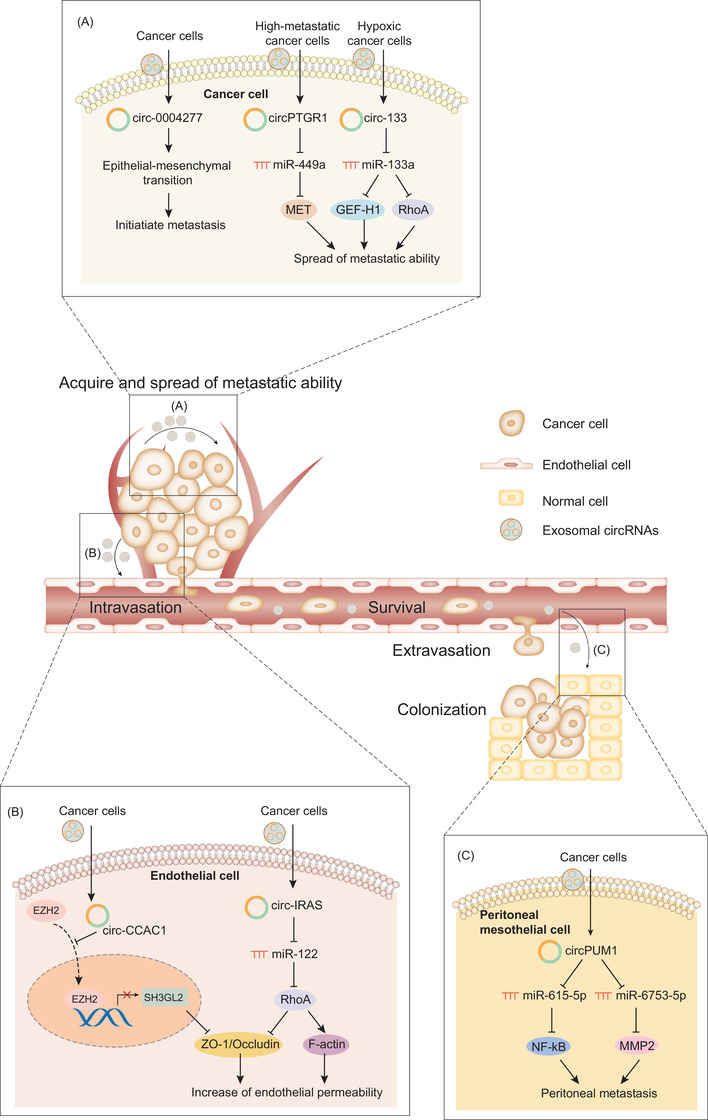
Molecular mechanisms of exosomal circular RNAs (circRNAs) in metastasis; exosomal circRNAs are involved in every step of metastasis, including acquisition and spread of metastatic ability, intravasation into blood vessels, survival and transmission through circulation, extravasation and colonization in distant organs. (A) Cancer cells with high malignancy transmit exosomal circRNAs to neighbouring low malignant cells to promote the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and initiate metastasis (e.g., circ‐0004277, etc.) or spread metastatic ability (circPTGR1, circ‐133, etc.). (B) Cancer cells transmit exosomal circRNAs to endothelial cells to destroy endothelial cell junctions such as ZO‐1 and increase vascular permeability (circ‐CCAC1, circ‐IRAS, etc.). Notably, circ‐CCAC1 prevents EZH2 nuclear translocation and blocks EZH2‐mediated SH3GL2 inhibition, thus upregulating SH3GL2 and decreasing ZO1 and occludin. (C) Cancer cells transmit exosomal circRNAs to distant peritoneal mesothelial cells to promote peritoneal metastasis (e.g., circPUM1, etc.)
