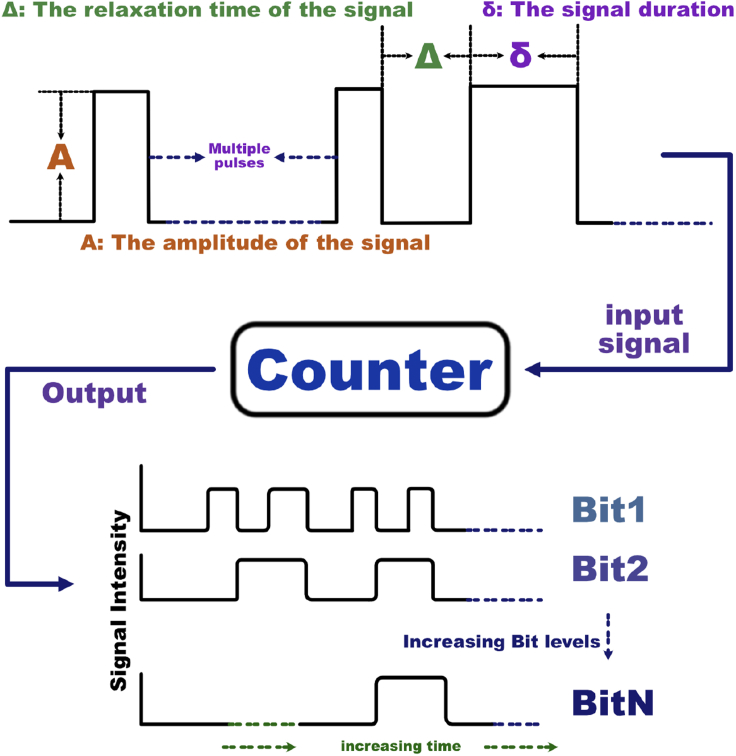
Figure 1.
A schematic view of a multi-bit counter
A general N-bit counter takes an input pulse train as an input, and outputs a modulo- count of the total number of pulses, represented by the binary state of each bit (right). The pulse trains will be assumed to respect constraints on pulse width δ, spacing (relaxation time that permits the system to approach steady state until the next pulse.) between signals , and pulse amplitudes A.