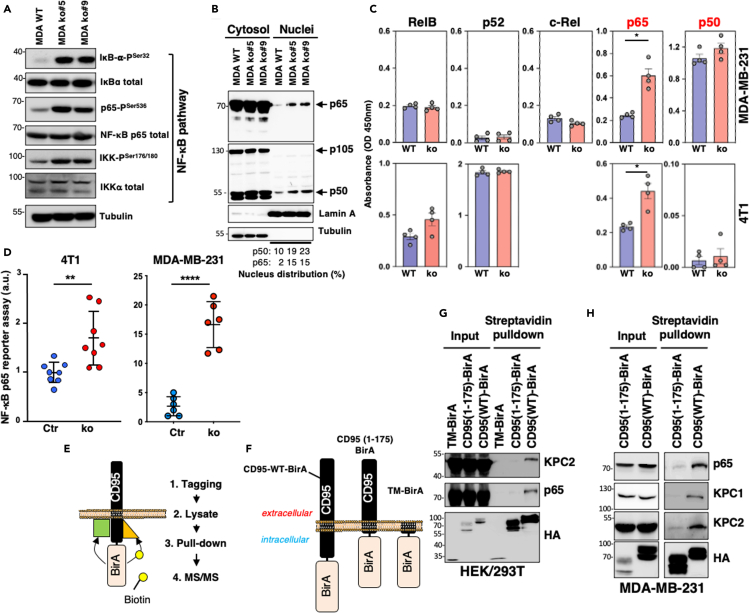
Figure 2.
KPC2 and p65, two novel interactants of CD95
(A) The activation status of the NF-κB signaling pathway was analyzed in wild-type (WT) and CD95 knock-out (KO5 and KO9) MDA-MB-231 cells by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Tubulin immunoblot serves as a loading control. Images are representative of three independent experiments.
(B) The presence of p65, p105, and p50 in the whole lysate (cytosol) or the nucleus fraction of wild-type and CD95 k.o. cells was evaluated by immunoblotting. Lamin A and tubulin serve as loading controls for nucleus and cytosolic fractions, respectively. Images are representative of three independent experiments.
(C) Nuclear extracts from WT and CD95 k.o. cells were subjected to the indicated ELISA to quantify activation of NF-kB. Mouse c-Rel DNA binding cannot be assessed with this kit. Mean ± SEM (n = 3), p values were calculated using nonparametric Mann-Whitney test.
(D) RelA activity was measured in indicated tumor cells using luciferase reporter assay (n = 6–8). ∗∗ and ∗∗∗∗ stand for p < 0.001 and p < 0.00001, respectively, using unpaired and nonparametric Mann-Whitney t test.
(E) Schematic representation of the BioID experiment.
(F) Schematic representation of BirA-fused CD95 constructs.
(G and H) BioID assay was conducted in CD95 k.o. HEK/293T cells (G) and MDA-MB-231 cells (H) reconstituted with indicated constructs and after streptavidin pull-down indicated immunoblotting was performed. Images are representative of three independent experiments.