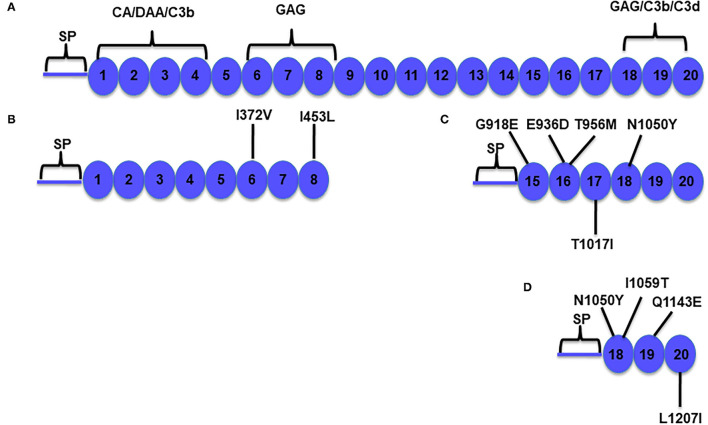
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of Factor H (FH) and its functional domains. (A) Factor H is a 155-kDa plasma complement regulatory protein composed of 20 repeating homologous domains of approximately 60 amino acids each, known as complement control protein (CCP) repeats, short consensus repeats (SCRs), or sushi domains (12). Factor H prevents the formation and accelerates the decay of the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb; decay accelerating activity) and is a cofactor for Factor I-mediated cleavage and inactivation of C3b (cofactor activity). Factor H has fluid-phase and cell-surface regulatory capabilities (13). The N-terminal portion contains the regulatory domain that mediates the cofactor activity and decay accelerating activity (repeats 1–4). The surface binding recognition motifs are located in repeats 6–8 and 18–20. (B–D) Factor H constructs used to prepare the variants (as indicated). Residue numbering includes the 18 amino acids of the signal peptide (SP). CA, cofactor activity; DAA, decay accelerating activity; C3b, C3b binding site; C3d, C3d binding site; GAG, glycosaminoglycan binding site.