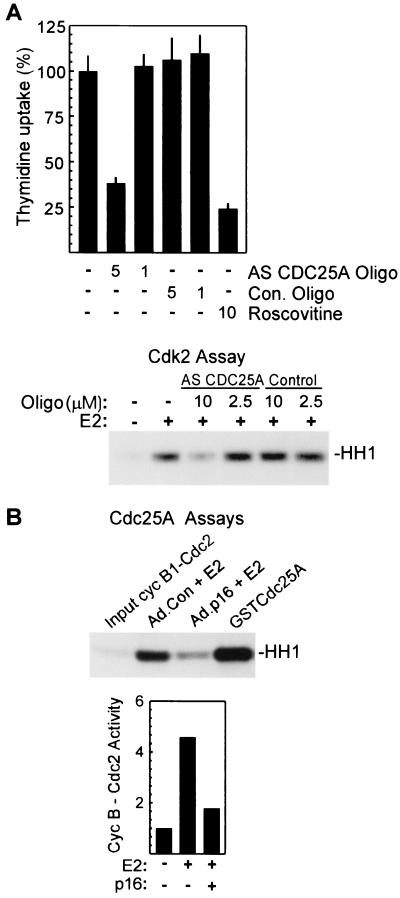
FIG. 5.
Cdc25A is required for estrogen-induced Cdk2 activation and DNA synthesis in MCF-7 cells and is inactive in cells expressing p16INK4a. (A, upper panel) Inhibition of S-phase entry by antisense (AS) CDC25A oligonucleotides (Oligo). DNA synthesis in E2-treated MCF-7 cells was assayed as given above in Fig. 1. Antisense oligonucleotides were added to the culture medium at the indicated concentrations 18 h before estrogen treatment and remained in the culture throughout the assay. Values represent percent thymidine incorporation relative to that in estrogen-treated control (Con.) cultures and are given as the mean ± standard deviation from four replicates. (A, lower panel) Inhibition of Cdk2 activation by antisense CDC25A. MCF-7 cells were treated with antisense CDC25A or control oligonucleotides as described above, and lysates prepared 12 h after E2 treatment were assayed for cyclin E-associated histone kinase activity. (B) Assay of endogenous Cdc25A activity. Cdc25A immunoprecipitates were prepared from MCF-7 cultures treated as indicated, and Cdc25A was eluted from the beads as described in Materials and Methods. The function of eluted Cdc25A was assayed as activation of cyclin B1-Cdc2 complexes measured in a standard histone kinase assay. In lane 4, maximal activation is demonstrated by treatment of complexes with purified recombinant GST-Cdc25A. Results from a separate experiment are presented graphically in the lower portion of panel B, with activity in lysates of untreated, Ad.Con-infected cells taken as 1.