Figure 1. Gel electrophoretic analysis of the P-Ap cross-link in duplex B.
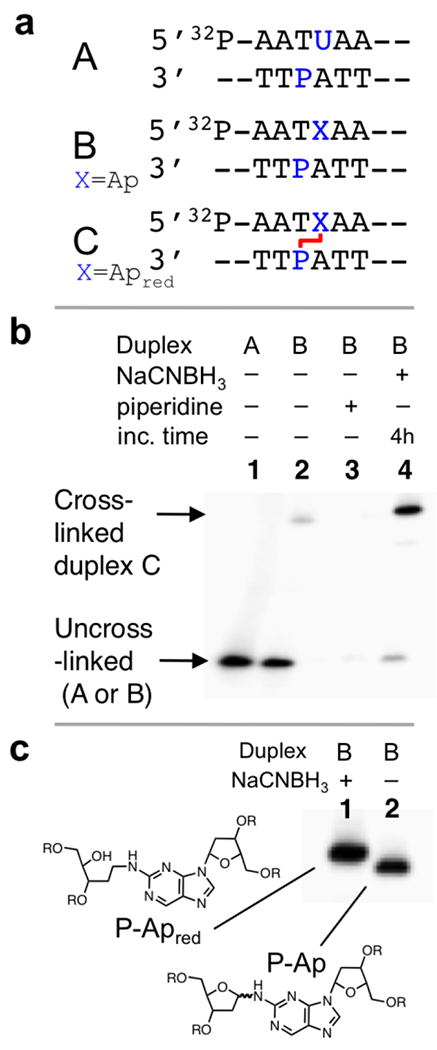
Panel a: The Ap-containing duplex B was generated by treatment of the corresponding dU-containing duplex A with UDG. The central cross-linking sequence is shown here and the complete sequence of the 35 nt duplexes are provided in the Supporting Information. Panel b: Gel electrophoretic detection of cross-link formation in duplex B. Lane 1: Size-marker consisting of 35 nt 32P-labeled dU-containing oligonucleotide; lane 2: Ap-containing duplex B, frozen immediately after mixing and stored at −20 °C prior to gel electrophoretic analysis; lane 3: Ap-containing duplex B treated subjected to piperidine workup (0.1 M, 95 °C, 15 min) to induce strand cleavage at the Ap site; lane 4: The 5’-32P-labeled duplex B was incubated in sodium acetate buffer (750 mM, pH 5.2) containing NaCNBH3 (250 mM) at 37 °C for 4 h. The 32P-labeled 2’-deoxyoligonucleotides were resolved on a 20% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and the radioactivity in each band quantitatively measured by storage phosphor autoradiography. Panel c: Gel electrophoretic separation of the reduced and unreduced P-Ap cross-links.
