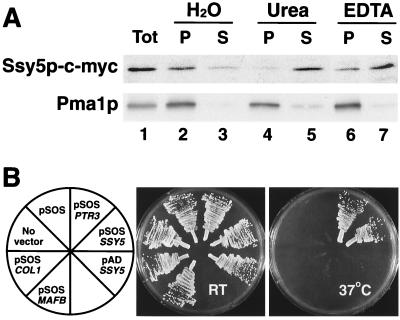
FIG. 3.
SSY5 encodes a peripherally associated PM protein. (A) The membrane association of Ssy5p was examined by using whole-cell lysates prepared from strain HKY77 expressing SSY5-c-myc. Aliquots of total protein lysate (Tot) were diluted 1:1 with H2O, 1.6 M urea, or 2 mM EDTA; mixed; and incubated on ice for 30 min. Membrane pellet (P) and soluble (S) fractions, obtained after centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 45 min at 4°C, were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting. As a control, the membrane association of the PM ATPase (Pma1p) was monitored. (B) The ability of Ssy5p to associate with the PM was assessed by using the SOS membrane recruitment system. Strains cdc25H (No vector) and cdc25H transformed with plasmids pSOS, pSOS-PTR3 (pHK044), pSOS-SSY5 (pHK045), pAD-SSY5 (pHK050), pSOS-Col1, and pSOS-MAFB were grown on YPD. Culture plates were incubated at room temperature (RT [permissive]) and 37°C (nonpermissive) as indicated, and after 4 days, the plates were photographed.