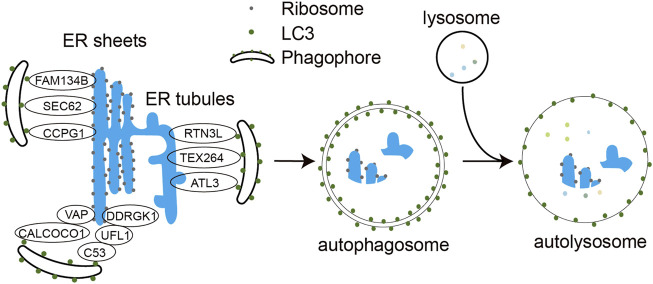
FIGURE 1.
Molecular mechanism of ER-phagy. Under different stress conditions, ER-phagy receptors FAM134B, SEC62, RTN3L, ATL3, TEX264, CCPG1, C53, and CALCOCO1 bind to LC3 via their LIR motifs and engulf ER structures in need of degradation into the phagocytic vesicles, which subsequently expand and close to form double-membrane autophagosomes. The autophagosome further fuses with the lysosome to form autophagolysosome. The encapsulated ER fragments are eventually degraded by hydrolases in the autolysosomes.