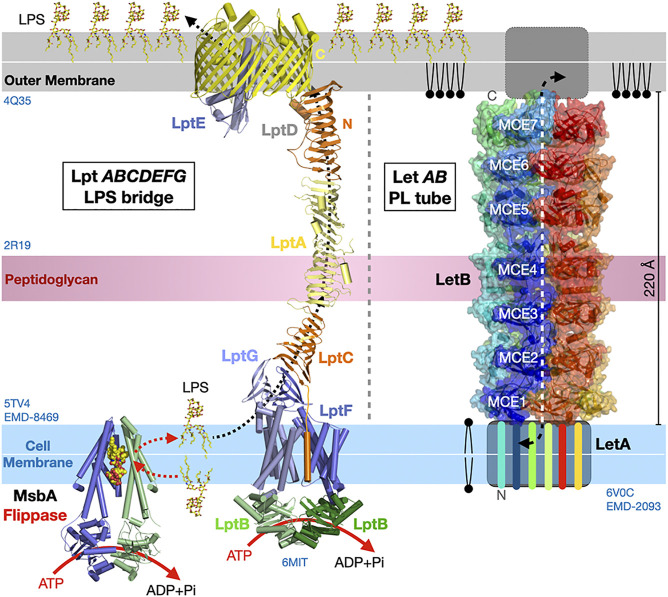
FIGURE 10.
Bulk lipid transfer systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Structure of the Lpt bridge transferring LPS (PDB 5TV4 2R19 4Q35 6MIT EMD-8469) and the LetB proteinaceous nanotube transferring PLs between membranes in Gram-negative bacteria (PDB 6V0C EMD-20993). The β-jellyrolls domains present in Lpt C, F, G, A and D align to form a periplasmic bridge with a solvent-exposed V-shaped hydrophobic groove. Hexamers of LetB form a protein tubular structure with a central channel capable of binding PLs and spanning the periplasmic space. The six LetB chains are colored in a rainbow pattern. The seven MCE domains repeated along one chain (in blue) are labeled. The sides of the protein tube are porous enabling solvent to enter the channel. It is unclear what drives PL transfer in the Let system. Structures and membranes are drawn to scale.