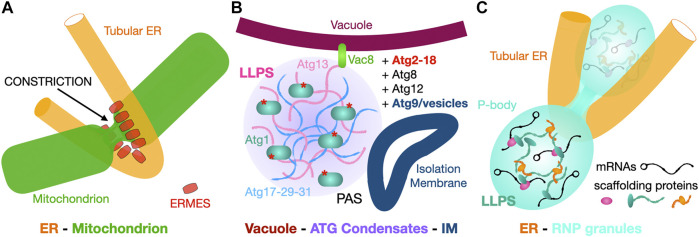
FIGURE 14.
Membrane and membrane-less contact sites. (A) “Classic” membrane to membrane contact site. The ER tubular network contacts mitochondria at constrictions marking their division. In yeast tethers such as ERMES are involved at these sites. (B, C). Membrane to membrane-less contact sites. (B) Vacuole-to-Atg complex condensate interactions drive isolation membrane formation at the ER-Vacuole-PAS contact site. Scramblase Atg9-vesicles derived from the Golgi provide the initial IM (phagophore) that will later expand into the autophagosome using ER lipids supplied by Atg2. (C) The ER tubular network contacts membrane-less P-bodies and regulates their biogenesis and activity. Simplified schematic of the content of PBs with RNPs made of repressed mRNA associated with multivalent scaffolding proteins that drive LLPS and formation of this membrane-less compartment.