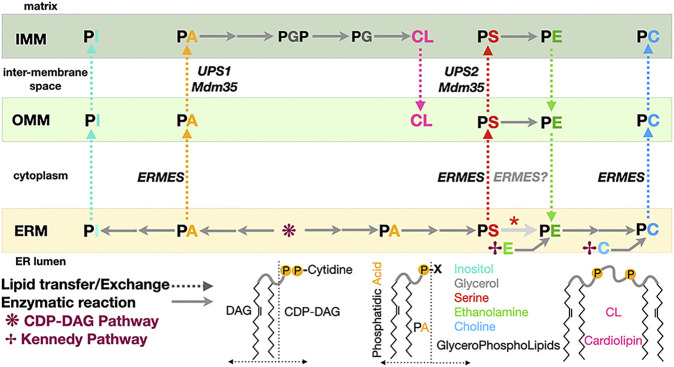
FIGURE 2.
Phospholipid biosynthesis is shared between the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrion. Simplified pathway for the biosynthesis of the major classes of glycerophospholipids in yeast. PA, phosphatidic acid; PE, phosphatidyl ethanolamine; PS, phosphatidyl serine; PC, phosphatidyl choline; PG, phosphatidyl glycerol; PGP, phosphatidyl glycerol phosphate; PI, phosphatidyl inositol; CL, cardiolipin. CDP-DAG, CDP diacylglycerol. DAG and its “activated” form CDP-DAG are some of the main building blocks providing the lipidic backbone of the PLs subsequently synthetized. Two pathways contribute of PL biosynthesis in yeast: the CDP-DAG pathway to generate PA and then PS subsequently transformed into PE then PC and the Kennedy pathway using DAG and ethanolamine or choline to directly generate PE or PC. Dotted arrows indicate PL transfer between membranes within the mitochondrion or between ER and mitochondrion; continuous arrows indicate biosynthetic reactions. A red asterisk indicates that depending on the carbon source, decarboxylation of PS into PE can be observed in the ER membrane. Some of the lipid exchange proteins or membrane tethering complexes (i.e., Ups1/Mdm35 and ERMES) shown to be involved in specific transfer/exchange are indicated.