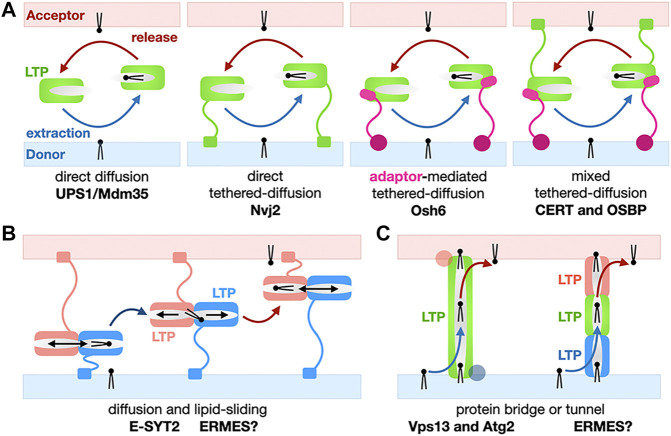
FIGURE 4.
Basic mechanisms for the non-vesicular exchange of lipids using lipid transfer proteins. (A) Transfer based on protein domain diffusion. Variations on the use of a soluble LTP domain for the shuttling of lipids between membranes: Soluble versus tethered LTP shuttles with or without combination of protein motifs and/or adaptor proteins targeting the LTP module to a specific MCS. Membrane-tethering motifs on the LTP or the adaptor can be present on both membranes. Only monovalent tethers/adaptors are shown here for the sake of simplification but more complex examples have been described. (B) Transfer using lipid sliding within a LTP domain combined with diffusion. Here we show a general simplified model; E-SYT2 (and possibly ERMES?) fall under this general category. (C) Transfer based on lipid bridges/tunnels. The lipid conduit spans the entire space separating the two organelles at a MCS can consist of one large LTP/tether protein (Vps13 and Atg2) or several LTPs (possibly SMP domains in ERMES?).