FIGURE 9.
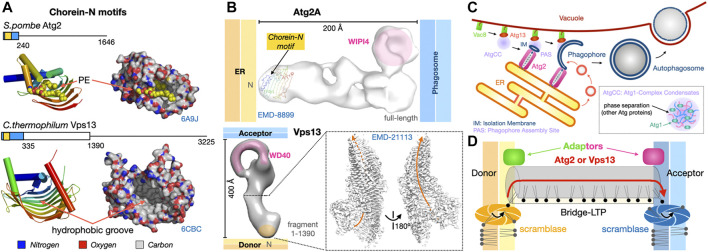
Dual tethers/LTPs Vps13 and Atg2 form bridges to transfer lipids in bulk at membrane contact sites. (A). Schematic structure of the Atg2 and Vps13 proteins from S. pombe and yeast are shown together with the crystal structures of the N-terminal fragments of S. pombe Atg2 (21-246) (PDB 6A9J) and C. thermophilum Vps13 (1–335) (PDB 6CBC) containing the Chorein-N motifs (∼100 residues boxed in yellow). Areas boxed in blue correspond to crystallized fragments. (B) NS-EM density map (30 Å resolution EMD-8899) of full-length (1-1938) human Atg2A bound to WIPI4. NS-EM density map (30 Å resolution) of full-length (1-3144) yeast Vps13 and cryo-EM map (3.8 Å resolution EMD-21113) of the N-terminal fragment (1-1390) of Vps13 from C. thermophilum. The cryo-EM map of Ct-Vps13 reveals the presence of a central groove suited for the transfer of PLs (orange arrow). The relative position occupied by the crystallized fragment containing the Chorein-N motif is shown in hAtg2A. Membranes and proteins are drawn to scale. The WIPI adaptor protein bound to Atg2A or WD40-like domain of Vps13 are highlighted in pink. (C) Bulk autophagy in yeast localizes at the ER-vacuole interface. Vacuolar protein 8 (Vac8) and Atg13 localize the Atg1-Complex Condensates near the membrane where Atg1 activation by phosphorylation triggers the formation of an isolation membrane (IM) at the phagophore assembly site (PAS). The LTP-bridge Atg2 fuels phagophore expansion by channeling ER PLs in synergy with vesicular accretion. Matured autophagosomes subsequently fuse with the vacuole and their content is then degraded/recycled. (D) “Lipid sink” model for the bulk transfer of lipids by Atg2 and Vps13. For Atg2, scramblases in the donor and acceptor membranes drive exchange by re-equilibrating lipid concentrations between leaflets.