FIGURE 4.
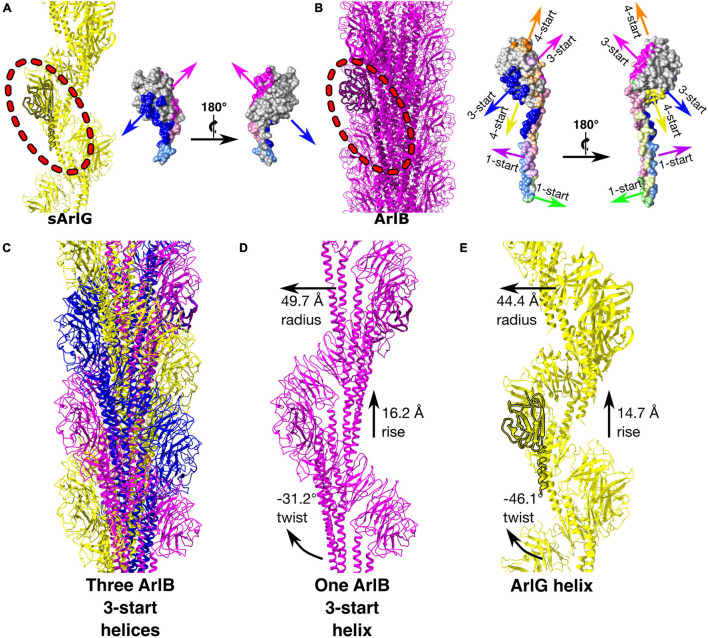
sArlG forms a helical filament with a different quaternary structure to the ArlB filament yet using a subset of the interactions used by ArlB. Comparison of the quaternary structures of the P. furiosus sArlG and ArlB filaments. (A) Left: Model of the sArlG filament (yellow) with a single protomer highlighted (outline). Right: two views of intersubunit sArlG interactions mapped onto the surface of a single protomer; blue represents interactions with the preceding protomer while pink represents interactions with the next protomer. Full colors represent interactions to the other subunit’s archaellin domain while pastels represent interactions to the N-terminal α-helix tail. (B) Left: Model of the ArlB filament from PDB 5O4U (purple) with a single protomer highlighted (outline). Six colors represent preceding and next protomers in the 1-start, 3-start, and 4-start helices of the filament. The 3-start helix interactions of ArlB (blue and pink) correspond to the intersubunit interactions of sArlG. (C) Illustration of the three 3-start ArlB helices in yellow, magenta, and blue. (D) The interactions and helical parameters of a single extracted 3-start helix of ArlB resembles (E) the sArlG helix.