Figure 5: Commensal bacteria provide a direct source of retinoic acid in the intestine.
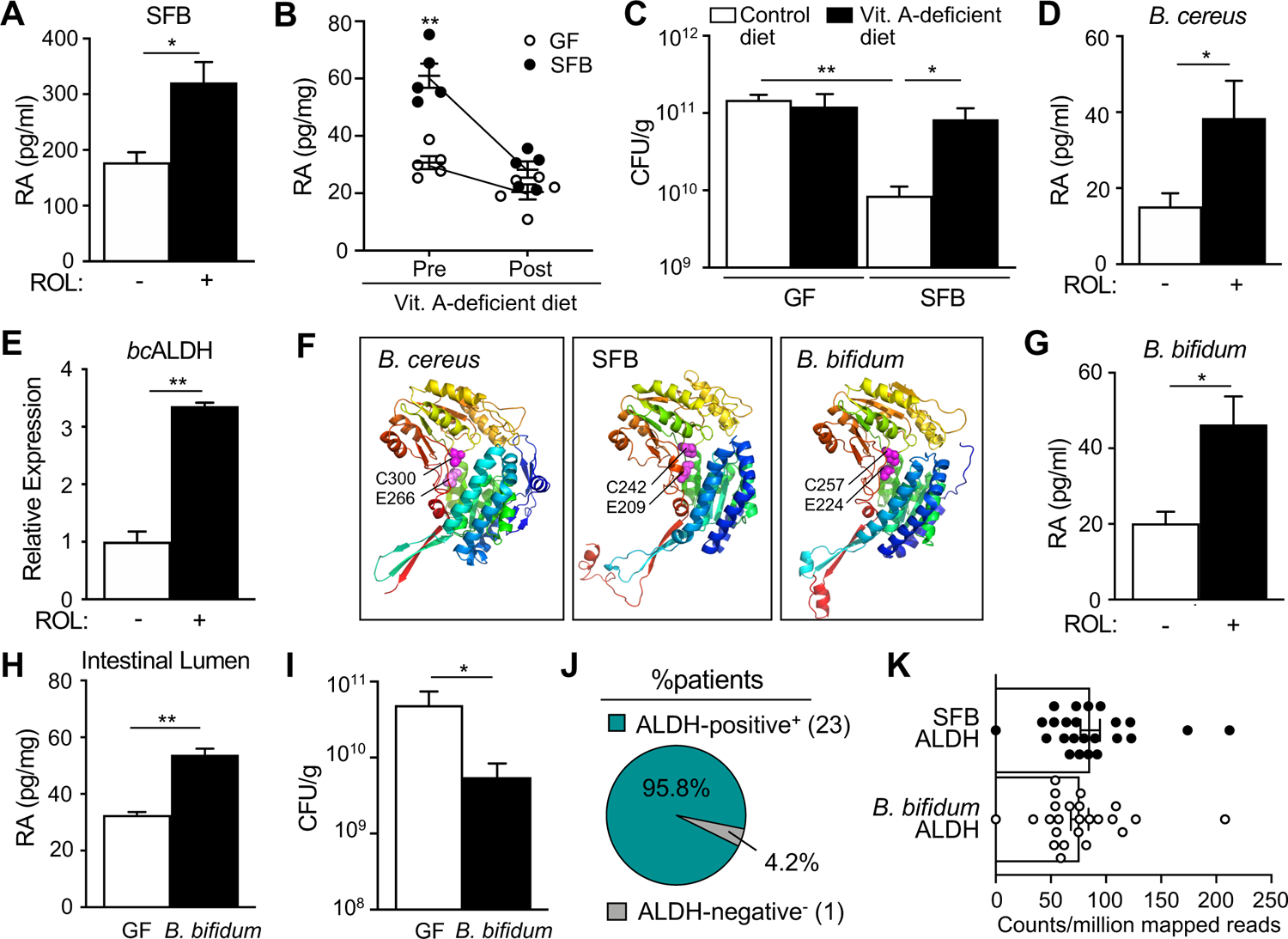
(A) Retinoic acid concentration in supernatants from intestinal explants from GF and SFB mice incubated with vehicle or all-trans retinol (ROL) (n = 3). (B) Retinoic acid levels in intestinal lumen of mice pre and post vitamin A-deficient diet. (C) C. rodentium CFUs in stool, normalized to sample weight, day 6 p.i. (n = 3) (D) Retinoic acid concentration in media from B. cereus cultured with ROL, per 108 CFU of bacteria (n = 3). (E) Expression of ALDH by B. cereus cultured −/+ ROL (n = 3). (F) Protein structure of B. cereus ALDH1A1 (KFL74159.1), SFB ALDH (WP_007440235.1) and B. bifidum ALDH (WP_015438559.1). Conserved catalytic glutamate [E] and cysteine [C] residues shown as magenta-colored spheres. Root-mean-square deviation of atomic positions (RMSD) compared to bcALDH1A1 for SFB ALDH = 2.059 Å; B. bifidum ALDH, RMSD = 1.514 Å. (G) Retinoic acid concentration following incubation with ROL, per 108 CFU of bacteria (n = 3). (H) Retinoic acid concentration in intestinal contents of GF mice monoassociated with B. bifidum, normalized to sample weight (n = 3). (I) C. rodentium CFUs in stool, normalized to sample weight, day 6 p.i. (n = 4–5) (J) Percent of patients containing intestinal microbiome reads that align to SFB or B. bifidum ALDH. (K) ALDH counts per million reads. Results are mean ± SEM. Data represent at least two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
