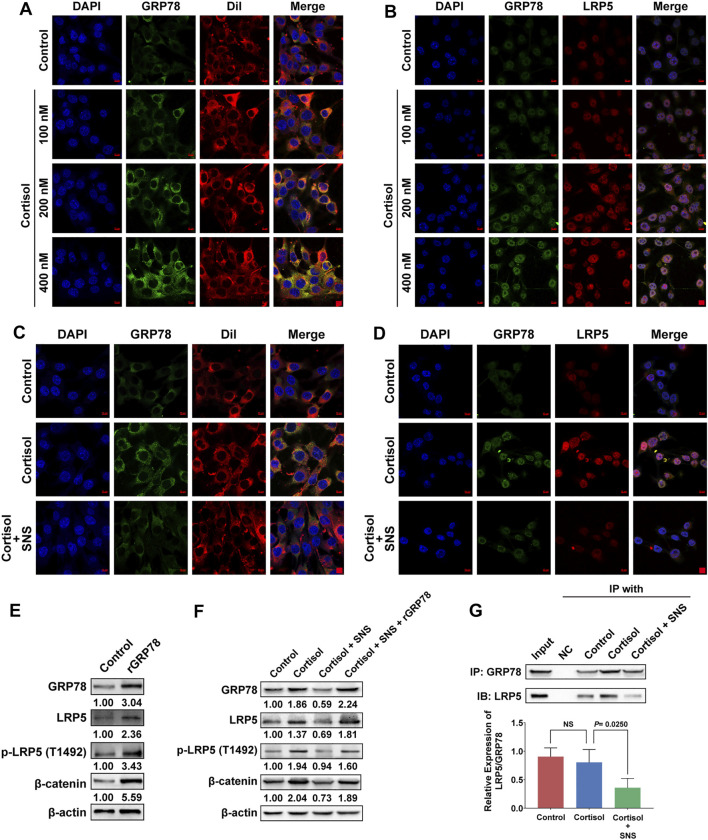
FIGURE 6.
SNS interrupts the interaction between GRP78 and LRP5 to suppress Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (A) After 4T1 cells were treated with cortisol for 24 h, the translocation of GRP78 to the cell membrane was monitored by immunofluorescence. Red: DiI-cell membrane tracker; green: GRP78. Co-localization of GRP78 and the cell membrane is shown as yellow fluorescence. (B) The 4T1 cells were treated with cortisol for 24 h, and the co-localization of GRP78 and LRP5 was detected by immunofluorescence. Co-localization is shown as yellow fluorescence. (C) The effect of SNS (200 μg/ml) on cortisol-induced cell membrane translocation of GRP78 was detected by immunofluorescence following SNS treatment for 24 h. (D) The effect of SNS (200 μg/ml) on the co-localization of GRP78 and LRP5 induced by cortisol was detected by immunofluorescence following SNS treatment for 24 h. (E) The expression of LRP5, p-LRP5, and β-catenin in the GRP78-overexpressing 4T1 cells was measured by western blots. (F) The 4T1 cells or GRP78-overexpressing 4T1 cells were treated with SNS (200 μg/ml) for 24 h, and the changes in cortisol-induced LRP5, p-LRP5, and β-catenin expression were detected by western blots. (G) The 4T1 cells were treated with SNS (200 μg/ml) for 24 h, and changes in the interaction of GRP78 with LRP5 were analyzed by Co-IP assays. Input represents the total protein extracts prepared without the antibody coupling resin. NC indicates the negative control prepared by adding quenching buffer to the antibody coupling resin. NS, not significant. The scale bars indicate 10 μm. One representative experiment of three independent experiments is displayed.