FIG. 1.
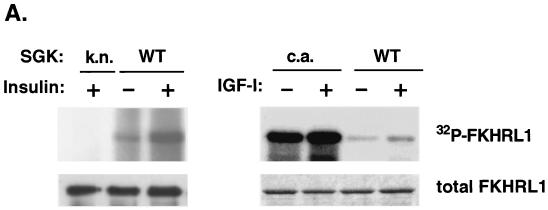
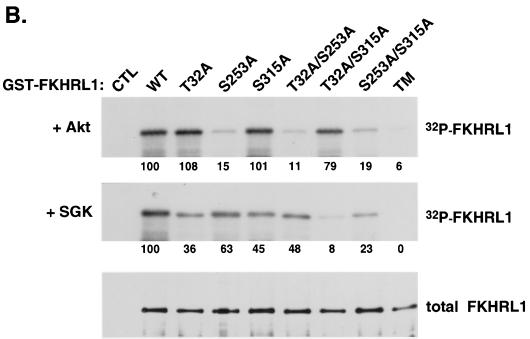
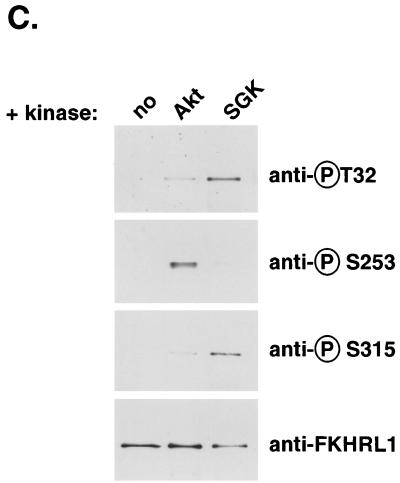
SGK phosphorylates FKHRL1 in vitro. (A) HEK 293 cells were transfected with WT SGK, a KN mutant of SGK (K127Q), or a CA mutant of SGK (S422D) and stimulated with insulin or IGF-I for 15 min. SGK was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with the anti-HA antibody and incubated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with WT GST-FKHRL1 (upper panels). The total level of GST-FKHRL1 was analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody directed against total FKHRL1 (lower panels). (B) HEK 293 cells were transfected with a CA mutant of Akt. Akt was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with the anti-HA antibody and incubated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with WT GST-FKHRL1 or a series of phosphorylation mutants of FKHRL1 (upper panel). Purified CA SGK was obtained from Upstate Biotechnology and incubated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with WT GST-FKHRL1 or a series of phosphorylation mutants of FKHRL1 (middle panel). The total levels of GST-FKHRL1 were analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody directed against total FKHRL1 (lower panel). CTL, control; TM, triple mutant of FKHRL1 (T32A/S253A/S315A). The numbers represent the percentage of phosphorylation of FKHRL1 mutants compared to wild-type FKHRL1. (C) Extracts obtained for panel B with WT-FKHRL1 were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies directed against phospho-T32, phospho-S253, and phospho-S315 or with the antibody directed against total FKHRL1.