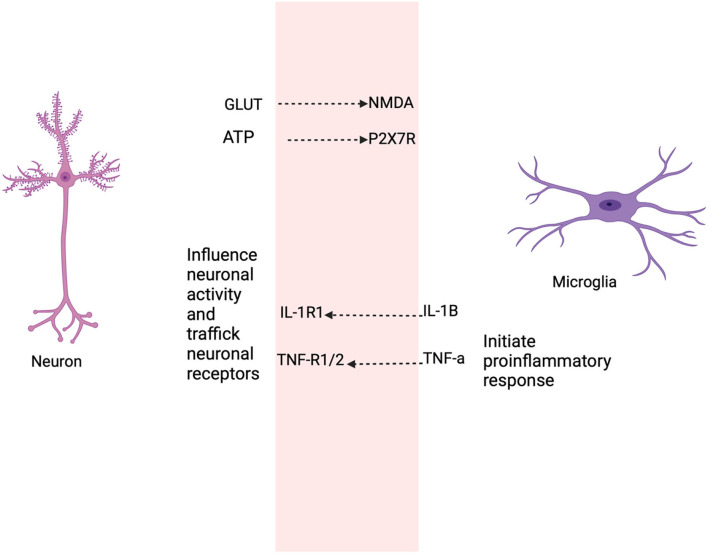
Figure 5.
This figure shows the selective roles that neurons and microglia share as a result of the diminished GPR109A-COX pathway. Neurons secrete soluble factors such as cytokines to regulate or maintain microglia activation sites (105–107), the release of neurotransmitter, such as glutamate from neurons influence microglial motility (108, 109). Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in microglia mediates through P2X7 receptor and produce pro-inflammatory cytokine (110). Likewise, active microglia secrete cytokine, prostaglandin which modulate neuronal function. For example, low levels of IL-1B are required for long term potentiation (LTP) (111, 112), while basal levels of TNF-α are necessary for AMPA and GABAA receptor trafficking (111). IL-1B and TNF induce neurotoxicity through elevated glutamate production resulting in neuronal excitotoxic death (113, 114).