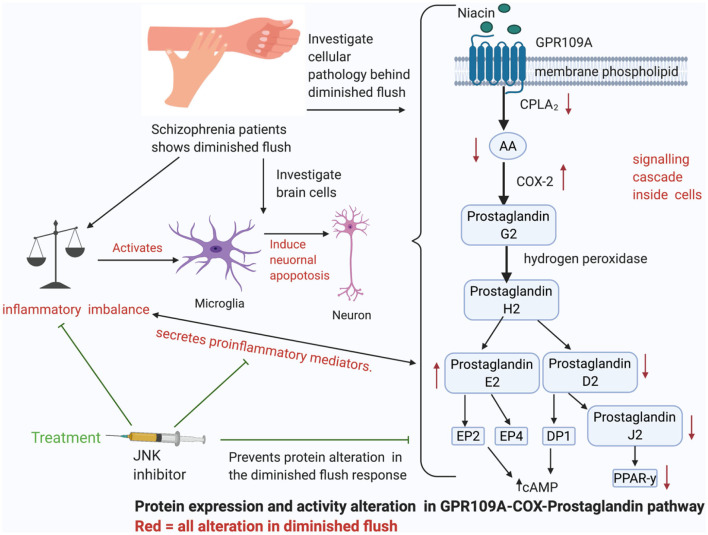
Graphical Abstract.
The cellular pathway behind diminished skin flush. The GPR109A-COX-prostaglandin pathways shows how niacin binds to G-coupled receptor-109A (GPR109A) on the cell membrane of leukocytes, and stimulates a cascade of signals, which activates enzymes to release vasodilators, prostaglandin D2 and E2. This pathway induces pro-inflammatory mediators, which can then activate M1 microglia to induce neuronal apoptosis. JNK inhibitors have been observed to act as an anti-inflammatory agent, reduce excessive pro-inflammatory mediators, and prevent microglial induced neuronal apoptosis.