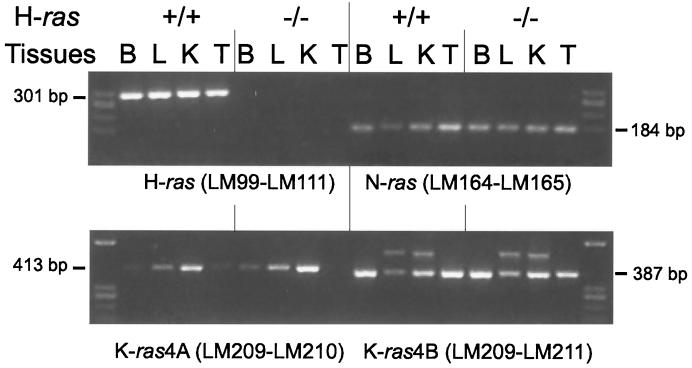
FIG. 2.
Detection by RT-PCR of H-ras, N-ras, K-ras4A, and K-ras4B in total RNA from tissues of animals with wild-type and mutant H-ras. Oligonucleotides specific for detecting each of the different ras gene transcripts were used as indicated. Their sequences are detailed in Materials and Methods. (Above) LM99 and LM111 amplified H-ras, and LM164 and LM165 amplified N-ras. (Below) LM209 and LM210 amplified K-ras4A, and LM209 and LM211 were specific for K-ras4B. Tissues used were brain (B), liver (L), kidney (K), and testis (T) from mice with wild-type (+/+) and null (−/−) H-ras genes. The levels of expression of N-ras and both K-ras4A and K-ras4B molecules in tissues were not affected by the absence or presence of H-ras gene products. As previously described, K-ras4A shows different expression levels depending on the tissues studied. The oligonucleotides used for K-ras4B occasionally lighted up an alternative band in liver and kidney whose intensity was not affected by either the presence or the absence of H-ras.