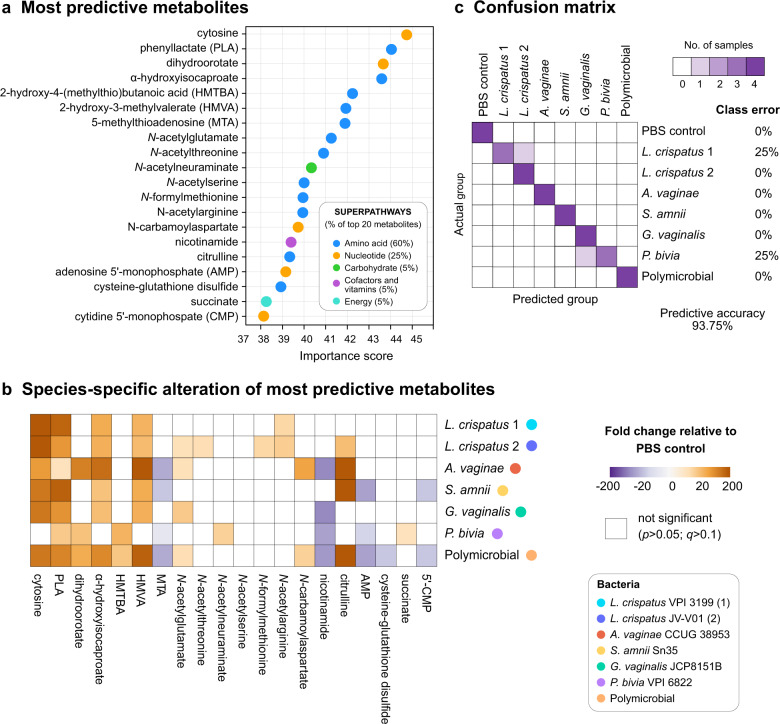
Fig. 4. Metabolites in 3D cell culture supernatants highly predict monomicrobial and polymicrobial infection with BVAB or Lactobacillus.
Metabolome data were used to predict bacterial infections using Random Forest. The analysis revealed that the most predictive metabolites belong to amino acid and nucleotide superpathways, which were altered in species-specific manner. The analysis highlighted excellent predictive accuracy (93.75%) of infection, compared to random 12.5%. a Twenty most predictive metabolites are depicted and ranked by relative importance score. The superpathways are indicated by colored dots. b The heatmap shows fold changes of the most predictive metabolites among bacterial infections compared to uninfected controls. Only the fold changes that were significant (p < 0.05; q < 0.01) are displayed. Gold- and purple-shaded squares indicate metabolite enrichment or depletion, respectively. Statistical differences were determined using Welch’s two-sample t test with FDR correction. c The confusion matrix illustrates the proportion of times each sample receives the correct classification. Among the 36 tested samples, only 2 were confused (1 from L. crispatus-colonized models and 1 from P. bivia-infected models).