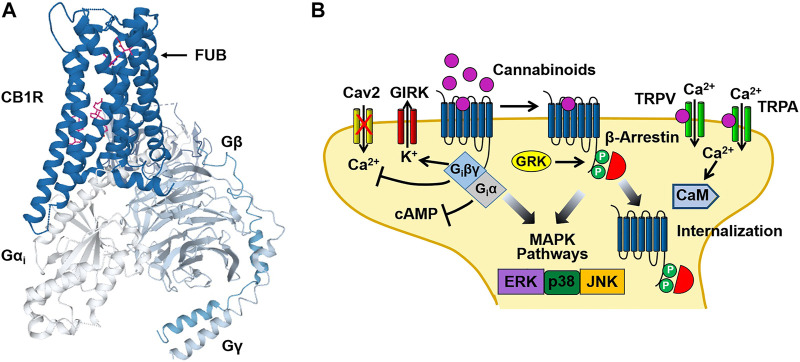
FIGURE 2.
Cannabinoid CB1 receptor structure and signaling. (A) Structural model of the CB1 receptor (CB1R)-Gi protein complex obtained from cryoelectron microscopy. The binding site for the synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-FUBINACA (FUB) is indicated by the magenta structure. The CB1-Gi receptor complex structure was obtained from the Protein Data Bank (code 6N4B). (B) Binding of cannabinoids to the neuronal CB1 receptor stimulates both neuronal Gi/Go and β-arrestin signaling pathways leading to an inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, activation of G protein-gated inward rectifier K+ (GIRK) channels and receptor internalization. In addition, activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) and ankyrin (TRPA) channels by cannabinoids causes Ca2+ influx that activates Ca2+-sensitive enzymes such as Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM). Figure 2B was adapted from Walsh and Andersen (Walsh and Andersen, 2020).