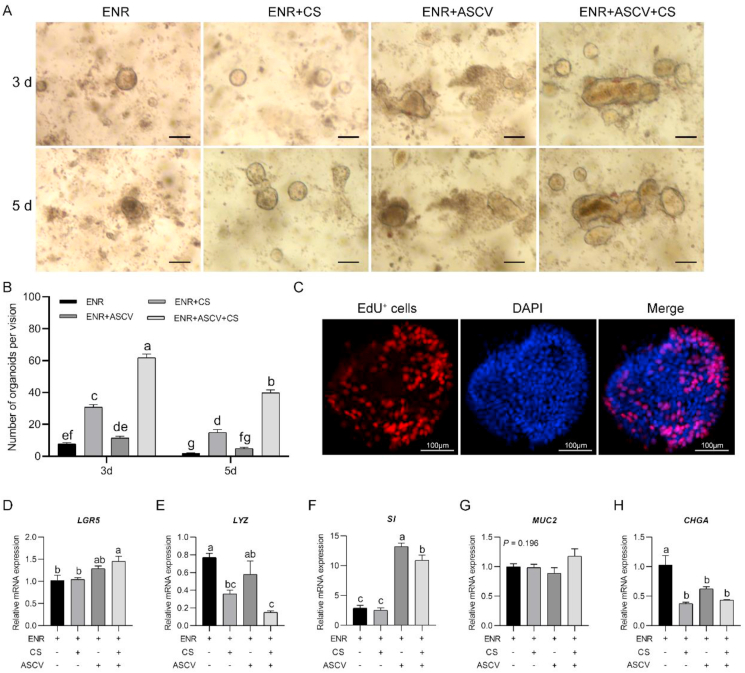
Fig. 4.
Influence of chicken serum supplementation on chicken crypt development. (A) Growth of chicken crypts with different treatments (scale bar, 200 μm). (B) Number of live intestinal organoids obtained with different treatments. At least 15 fields were used for counting the organoids obtained with each treatment. (C) 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) positive cells in organoids cultured for 5 d in medium supplemented with chicken serum and A8301, SB202190, CHIR99021 and valproic acid (scale bar, 100 μm). (D to G) Relative mRNA expression of mature intestinal epithelial markers of organoids after 5 d of culture with different treatments. Experiments were performed at least 3 times and a representative one was exhibited. Error bars, SEM (n = 3 wells). a, b, c Different letters on bars mean a significant difference (P ≤ 0.05). ENR, the mixture of epidermal growth factor, Noggin and R-spondin 1; ASCV, the mixture of A8301, SB202190, CHIR99021 and valproic acid; CS = chicken serum; DAPI = 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; LGR5 = leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5; LYZ = lysozyme; SI = sucrase-isomaltase; MUC2 = mucin 2; CHGA = chromogranin A.