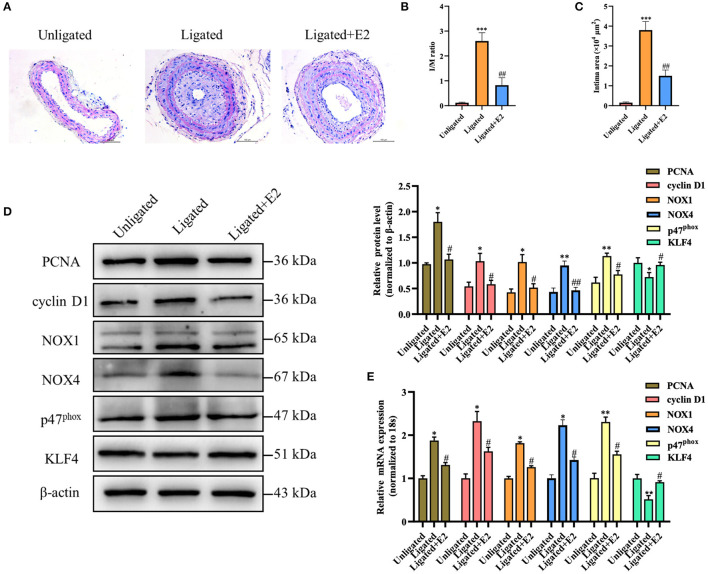
Figure 1.
E2 attenuates neointimal formation, proliferation and oxidative stress induced by carotid artery ligation. (A) Representative photomicrographs of the HE-stained sections of carotid arteries from unligated vessels, ligated vessels, and ligated vessels treated with E2 (n = 4). Scale bars = 100 μm. (B,C) Morphometric quantification of I/M ratio and the intima area in the different groups. ***p < 0.001 vs. Unligated group, ##p < 0.01 vs. Ligated group. (D) PCNA, cyclin D1, NOX1, NOX4, p47phox and KLF4 expression in unligated, ligated and ligated + E2-treated carotid arteries was detected by Western blotting. Statistic of band intensities is shown on the right (n = 3). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. Unligated group, #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 vs. Ligated group. (E) PCNA, cyclin D1, NOX1, NOX4, p47phox and KLF4 expression in unligated, ligated and ligated + E2-treated carotid arteries was detected by qRT-PCR (n = 3). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. Unligated group, #p < 0.05 vs. Ligated group.