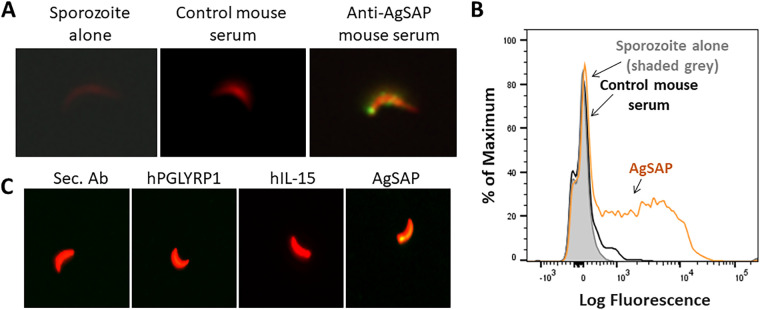
FIG 2.
AgSAP binding to P. berghei sporozoites. To examine the interaction of AgSAP with Plasmodium sporozoites, P. berghei sporozoites were probed with polyclonal antibodies specific for AgSAP. (A) Sporozoites (red) were labeled with endogenous AgSAP on the surface (green) and probed with goat anti-mouse IgG antibody labeled with the fluorescent dye Alexa Fluor 488. Samples were visualized using a fluorescence microscope at a ×20 magnification. As a control, sporozoites were incubated with serum from naive mice or with secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody only. (B) The binding of AgSAP to sporozoites was analyzed by flow cytometry. Plasmodium sporozoites were isolated from infected A. gambiae mosquitoes. Sporozoites were incubated with preimmune serum or AgSAP-specific antibodies generated in mice. After binding, sporozoites were fixed and analyzed by flow cytometry. Binding is compared in the overlay histogram. The sample that had sporozoites incubated with AgSAP-specific antiserum is shown by an orange trace, and the sample with sporozoites and secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody alone is shown in a black trace, while the sporozoites alone are shown in solid gray. (C) To investigate AgSAP binding to Plasmodium sporozoites, we used recombinant purified protein. Recombinant AgSAP (100 μg/ml) was incubated with Plasmodium sporozoites expressing redstar. The concentration was based on our previous work with mosGILT (14). As controls, recombinant human interleukin-15 (hIL-15) or human peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (hPGLYRP1) was incubated with sporozoites at the same concentrations. Sporozoites (red) were subsequently probed with mouse anti-His tag primary antibodies and anti-mouse IgG AF488-labeled secondary antibody (Sec. Ab) (green).