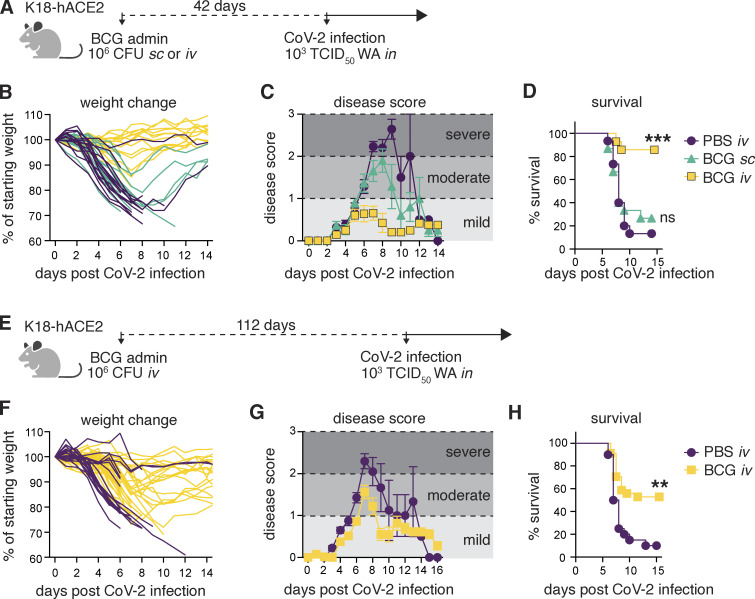
Figure 1.
BCG i.v. administration protects K18-hACE2 mice from lethal SCV2 challenge. (A–H) K18-hACE2 mice were inoculated with 106 CFUs BCG Pasteur by s.c. or i.v. injection. Control animals received the same volume of PBS i.v. At 42 (A–D) or 112 d (E–H) after BCG administration, mice were infected with 103 TCID50 SCV2 WA by i.n. instillation. (A and E) Schematic of experimental design. (B and F) Weight change following SCV2 infection shown as percentage of starting weight. (C and G) Animals were scored on a scale of 0–3 by a blinded observer, with 0 referring to no observable signs of disease and 3 referring to a moribund state requiring euthanasia. Scoring criteria are outlined in the Materials and methods. (D and H) Kaplan–Meier curve of animal survival following SCV2 challenge. Statistical significance was assessed by Mantel-Cox test. ns, P > 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Mean ± SEM is shown. Data are pooled from two to three independent experiments each with 4–15 mice per group.