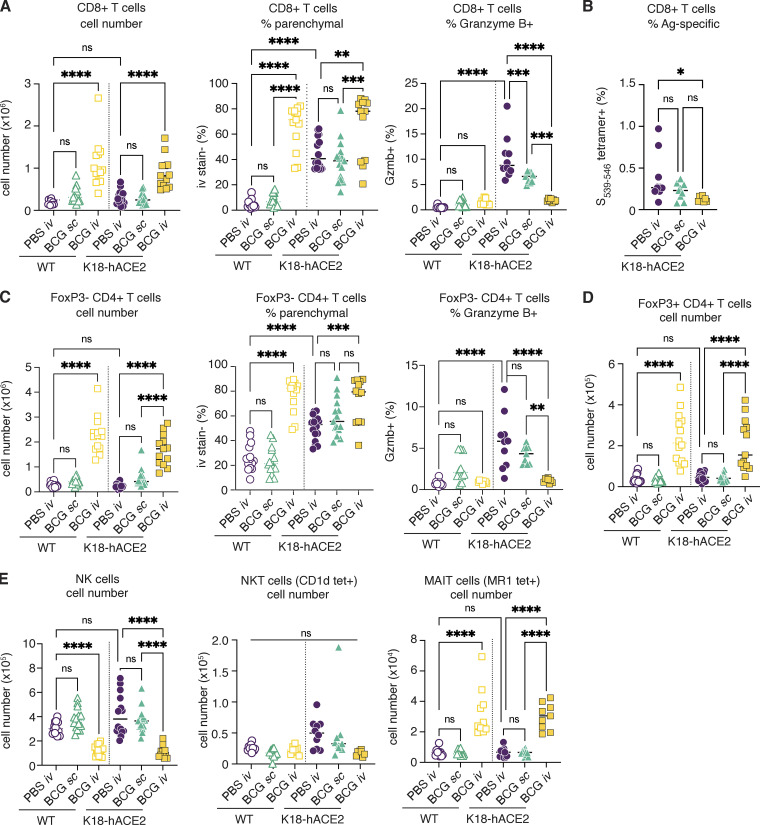
Figure S3.
Prior BCG i.v. administration limits bystander cytotoxic responses in SARS-CoV-2–challenged mice. (A–E) K18-hACE2 mice or non-transgenic littermate controls (WT) were inoculated with 106 CFUs BCG Pasteur by s.c. or i.v. routes. Control animals received the same volume of PBS i.v. At 42 d after BCG administration, mice were infected with 103 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 (WA1/2020) by i.n. instillation. Lungs were collected 5 d after viral challenge and assessed by flow cytometry. Gating strategy is shown in Fig. S2. (A) Number of CD8+ T cells, frequency of CD8+ T cells negative for i.v. stain, and frequency of CD8+ T cells expressing granzyme B. (B) Frequency of CD8+ T cells positive for the S(539-546) tetramer. (C) Number of FoxP3− CD4+ T cells, frequency of FoxP3− CD4+ T cells negative for i.v. stain, and frequency of FoxP3− CD4+ T cells expressing granzyme B. (D) Number of FoxP3+ CD4+ T cells. (E) Number of NK, NKT, and MAIT cells. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Data are pooled from three independent experiments each with four to five mice per group. Ag, antigen; tet, tetramer.