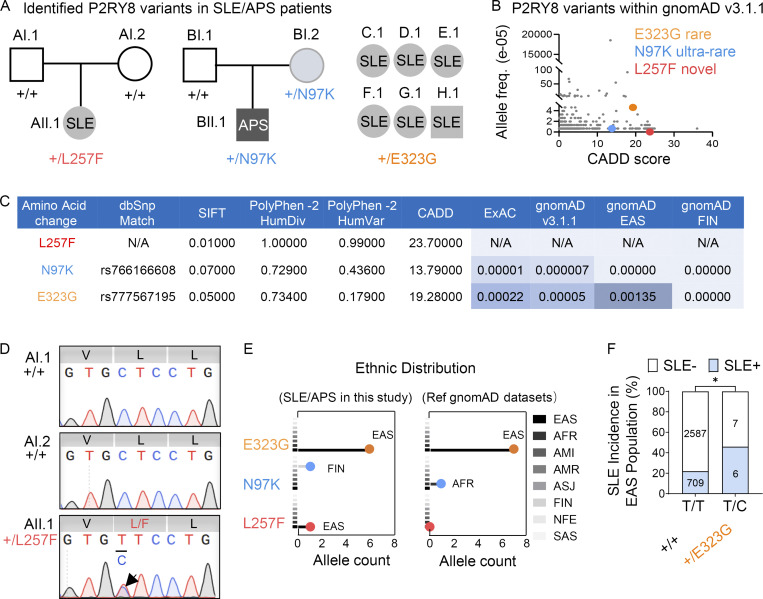
Figure 1.
Identification of P2RY8 variants in patients with SLE. (A) Left and center: Pedigrees showing affected probands and parents. Right: Summary of six affected probands. (B) P2RY8 variants presented in reference gnomAD v3.1 database (http://gnomad.broadinstitute.org). (C) Deleterious significance of each variant was predicted based on three tools, including PolyPhen-2, SIFT, and CADD. The ExAC, gnomAD allele frequency, and SNP database (dbSNP) match shown as indicated. HumDiv/HumVar, PolyPhen-2 classifiers for evaluating missense mutations; FIN, Finnish. (D) Sanger confirmation of P2RY8 L257F variant. V, valine; L, leucine; L/F, leucine/phenylalanine. (E) Population distribution of P2RY8 variants in affected probands or in reference (ref) gnomAD v3.1 datasets. Line colors correspond to ethnic group. AFR, African/African American; AMI, Amish; AMR, American Admixed/Latino; ASJ, Ashkenazi Jewish; NFE, Non-Finnish European; SAS, South Asian. Total alleles in EAS marked in bold. (F) Graph showing SLE incidence in +/+ versus +/E323G EAS population. n = 715, EAS SLE analyzed in this study (blue); n = 2,594, EAS control donors in reference gnomAD v3.1 database (white). P = 0.0312 (χ2 test), P = 0.0423 (Fisher’s exact test). *, P < 0.05. freq., frequency.