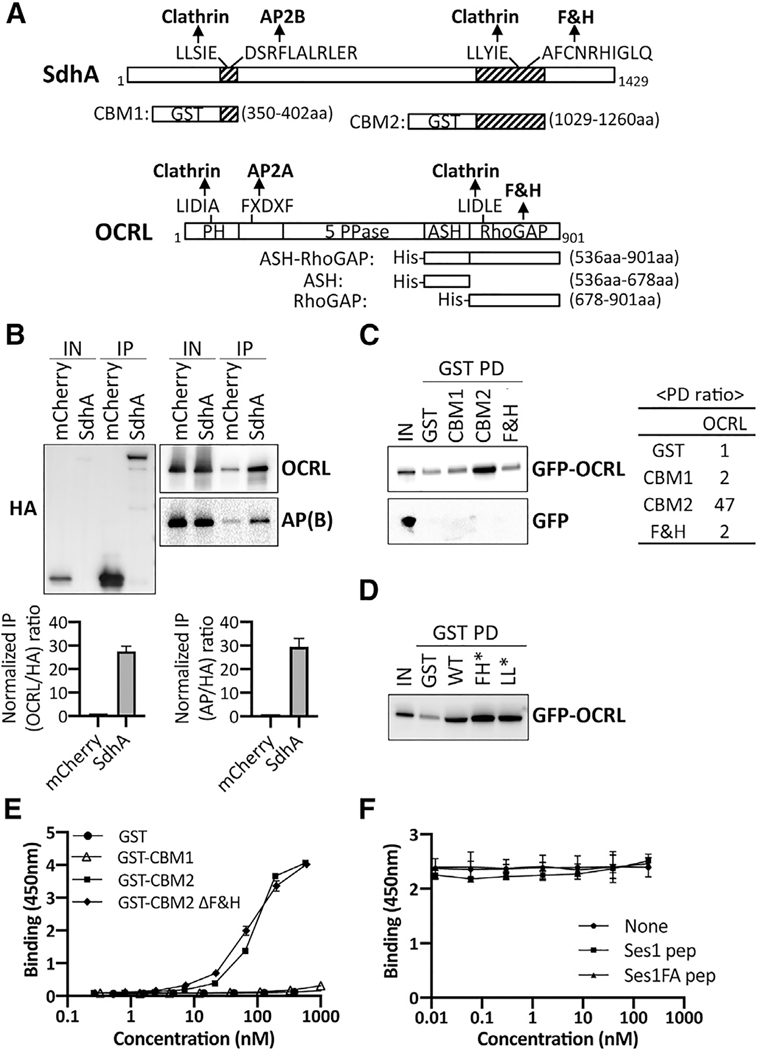
Figure 1. SdhA directly interacts with OCRL but independently of F&H motif.
(A) Conserved motifs of SdhA and OCRL and maps of GST or His fusions. Motifs identified by Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource (http://www.ELM.eu.org) are shown. 5 PPase, 5 inositol polyphosphate phosphatase; ASH, ASPM-SPD2-Hydin; PH, pleckstrin homology; RhoGAP, Rho GTPase activating protein.
(B) Top: HA-mCherry or HA-mCherry-SdhA overexpressed in HEK cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA. AP(B), AP complex β subunit. The amount of input (0.2% lysates) and IP (20%) is shown. Bottom: densitometry of coIP is shown. Average of two sets of independent experiments is shown with error bars showing maximum of two determinations.
(C) Purified GST fusions were used in pull-downs (GST PDs) as described (STAR Methods). The amount of input (1% of total lysate) and resulting precipitate (20% of total) are shown. Right: ratio of the pull-down from this gel by densitometry is shown.
(D) GST PDs as in (C) using SdhA-CBM2 mutations in F&H motif (F1195A H1199A; FH*) or clathrin box motif (L1177A L1178A; LL*).
(E) 96-well plates coated with ASH/RhoGAP domain challenged with GST-tagged SdhA peptides (STAR Methods). SdhA binding to OCRL detected using anti-GST antibodies and chromogenic substrate is shown (mean ± SD; n = 3 wells).
(F) Competition test of SdhA-CBM2 versus F&H motif peptide of Ses1 and OCRL binding-defective point mutation (Swan et al., 2010). Data and error bars are means ± SD (n = 3 determinations).
(E and F) Three independent experiments were performed. Shown is a representative of experiment using replicates from 3 wells from a single experiment. Linked to Tables S1–S3.