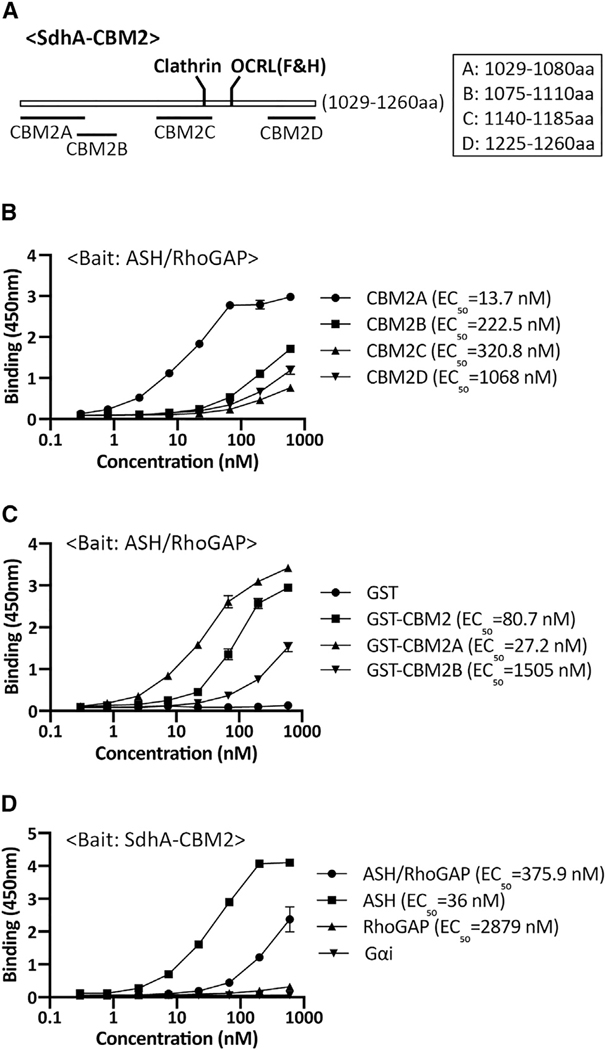
Figure 2. Mapping of the interacting regions of SdhA and OCRL using solid-phase binding assays.
(A) Constructs designed based on the coiled-coils prediction by ncoils (Lupas et al., 1991).
(B) SdhA-CBM2A binds to ASH-RhoGAP domain. Plate coated with ASH/RhoGAP was challenged with indicated SdhA constructs. EC50 was calculated as described (STAR Methods).
(C) High-affinity binding of CBM2A to ASH-RhoGAP. Protocol is as in (B).
(D) SdhA-CBM2 associates with ASH domain specifically. Plate coated with SdhA-CBM2 was challenged with His-tagged OCRL domains. Binding is detected by anti-His antibodies. His-Gαi was used as a negative control.
Linked to Table S3 and Figure S1. Data shown and error bars are means ± SD (n = 3 wells). Shown are representative assays of experiments performed in triplicate wells. Experiments were repeated three times.