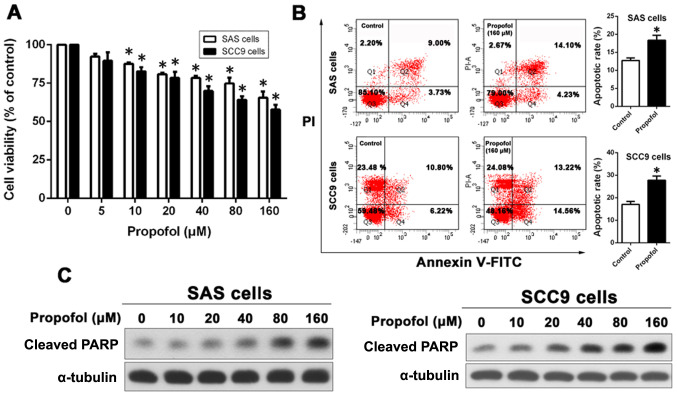
Figure 1.
Propofol decreases oral squamous cell carcinoma cell viability and promotes cell apoptosis. (A) Effect of propofol on SAS (n=4) and SCC9 (n=3) cell viability. Cells were treated with 0–160 µM propofol for 48 h and then cell viability assay was determined using MTT assays. (B) Cells were treated with 160 µM propofol for 48 h. Apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and the ratio of apoptotic cells was quantified using flow cytometry. (SAS cells, n=3; SCC9 cells, n=5) (C) Effect of propofol on cleaved PARP protein expression levels was determined by western blotting with α-tubulin as the loading control (n=3). Cells were treated with increasing doses of propofol (0–160 µM) for 48 h. *P<0.05 vs. control. PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.