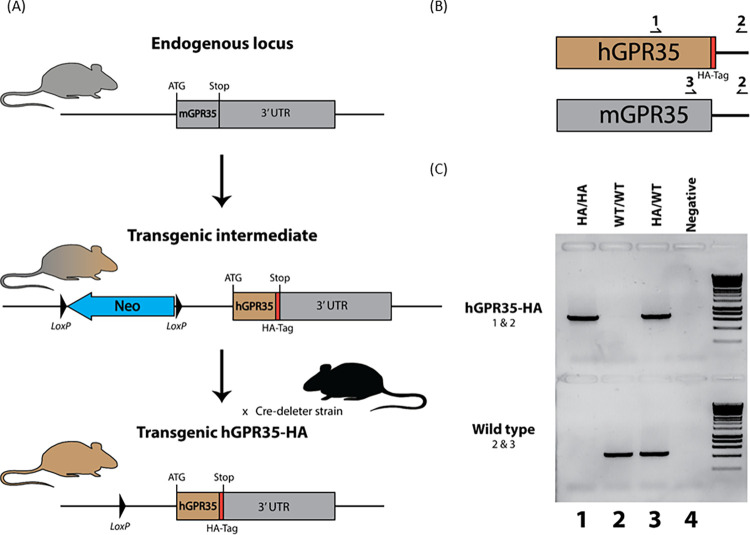
Figure 6.
Generation and characterization of human GPR35a-HA expressing transgenic knock-in mice. (A) Transgenic C57BL/6N mice with the human GPR35a coding sequence replacing the mouse sequence, along with the addition of a HA epitope tag before the stop codon were generated via a neomycin selective gene containing intermediate. These mice were crossed with a cre-deleter line to excise the selective gene leaving only LoxP sequences and the desired hGPR35a-HA sequence. The cre-deleter was then backcrossed out to isolate the hGPR35a-HA transgenic mice. (B, C) Human- and mouse-specific forward primers were used along with a reverse primer located in the 3′ UTR to genotype transgenic homozygous (HA/HA), transgenic heterozygous (HA/WT), and wild-type (WT/WT) mice. Expression of GPR35 in humanized transgenic mice as well as wild-type mice was assessed using qRT-PCR (see Tables 1 and 2).