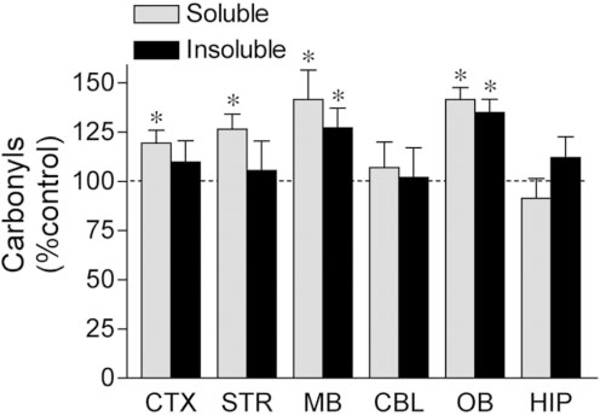
Figure 9.
Chronic rotenone infusion induced selective oxidative damage, with the greatest damage in the midbrain and the olfactory bulb. Chronic rotenone infusion increased protein carbonyl levels in soluble protein isolated from the striatum (n = 18), midbrain (n = 18), cortex (n 11), and olfactory bulb (n 12) but not the cerebellum (n = 10) or hippocampus (n = 10). Rotenone exposure increased insoluble protein carbonyl levels only in mid brain (n = 18) and olfactory bulb (n = 12). Data are expressed as a percentage of protein carbonyl levels in vehicle-treated animals. Results represent means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 compared with control.