Abstract
Monitoring severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on surfaces is emerging as an important tool for identifying past exposure to individuals shedding viral RNA. Our past work has demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) signals from surfaces can identify when infected individuals have touched surfaces such as Halloween candy, and when they have been present in hospital rooms or schools. However, the sensitivity and specificity of surface sampling as a method for detecting the presence of a SARS-CoV-2 positive individual, as well as guidance about where to sample, has not been established. To address these questions, and to test whether our past observations linking SARS-CoV-2 abundance to Rothia spp. in hospitals also hold in a residential setting, we performed detailed spatial sampling of three isolation housing units, assessing each sample for SARS-CoV-2 abundance by RT-qPCR, linking the results to 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences to assess the bacterial community at each location and to the Cq value of the contemporaneous clinical test. Our results show that the highest SARS-CoV-2 load in this setting is on touched surfaces such as light switches and faucets, but detectable signal is present in many non-touched surfaces that may be more relevant in settings such as schools where mask wearing is enforced. As in past studies, the bacterial community predicts which samples are positive for SARS-CoV-2, with Rothia sp. showing a positive association.
Body
Environmental monitoring for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) is increasingly gaining acceptance. In the Safer at School Early Alert (SASEA) (https://saseasystem.org/) project, daily surface swabbing was employed as part of an effort to detect coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases in nine elementary schools. This study identified 89 clinically positive COVID-19 cases, 33% preceded by a room-matched surface positive (1). As pandemic response measures like SASEA become more widely implemented, understanding where SARS-CoV-2 signatures will most likely be found reduces cost and labor of surface swabbing in large facilities. Previous work has focused on sampling arbitrary surfaces in isolation and congregate care facilities, homes, and hospitals, with varying detection performance obscuring which surfaces are best for monitoring COVID-19 spread (2–6). Counterintuitively, high-touch hospital surfaces expected to accumulate viral load, including door handles and patient bed rails, can yield lower SARS-CoV-2 detection rates, presumably because they are cleaned more often (7–8).
Most microbes in the built environment come from human inhabitants (9–11). Oral, gut, and skin microbiomes of COVID-19 patients change during disease (8,12–13); therefore, SARS-CoV-2 positive built environmental samples may differ in bacterial communities from SARS-CoV-2 negative samples. This has been documented in a hospital setting, with associations between SARS-CoV-2 status (Detected/Not Detected) and both overall microbial community and Rothia spp. specifically (8).
To extend these results to a residential setting and understand how SARS-CoV-2 is distributed in the living space of an infected individual, we performed environmental sampling in the apartments of three people who recently tested positive for COVID-19 (Sup. Fig. S1) while quarantined in an isolation facility. On the day of swabbing, each quarantining individual provided an anterior nares swab sample (Average Cq: 29.5, 28.4, 28.6 for Apartments A, B, and C respectively). Although apartments differed in size, floor plan, and features (furniture, appliances, etc.), similar features at similar densities were swabbed across all three (n=140,116,125).
Each sampled surface was swabbed twice in immediately adjacent locations: first with a swab premoistened and stored in 95% ethanol, then by a second swab premoistened and stored in a 0.5% SDS w/v solution (Supplementary Methods). Ethanol samples underwent 16S V4 rRNA gene amplicon (16S) sequencing, and SDS samples underwent RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection. 16S sequences were demultiplexed, quality filtered, and denoised with Deblur (14) in Qiita (15) using default parameters. Resulting feature tables were processed using QIIME2 (16).
Findings
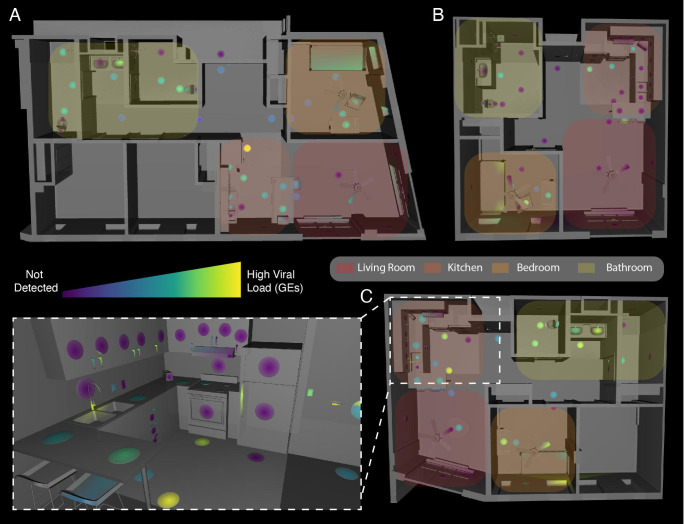
We collected 381 matched 16S and SARS-CoV-2 surface samples from the three apartments, of which 178 (47%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2 (Fig 1) (Table 1). Apartments A and C had comparable positivity rates (53% and 61%, respectively), but Apartment B was substantially lower (24%). In all three apartments, the rate of detection was highest in the bedroom (72% on average vs 47% overall). We estimated surface viral load, in viral Genomic Equivalents (GE’s), from Cq’s using published regression curves (17) and mapped resulting viral loads onto 3D renderings of each apartment. High-touch surfaces, including handles and switches, had highest viral load across all apartments, followed by floor samples and then high-use objects (fridge, sinks, toilets, beds) (Fig. 1). The maps for each apartment were studied to understand patterns of SARS-CoV-2 detection and deposition by room use. In the kitchens, objects with planar faces and handles, such as the refrigerator, cabinets, and drawers, revealed that only the touched handles had detectable RT-qPCR signal (Fig. 1C inset, as an example). We could not detect viral RNA on adjacent planar faces, which were presumably breathed on but not touched.
Figure 1.
Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 viral load in isolation dorm apartments. (A-C) Floor plans for each apartment highlighting where SARS-CoV-2 RNA signatures were detected. (Inset) 3D rendering of the kitchen in Apartment C showing SARS-CoV-2 viral load in Genomic Equivalents (GEs) mapped to features in that room.
For quality control of 16S sequencing from low-biomass samples, we sequenced surface swabs from the apartments together with positive and negative controls using KatharoSeq (Supplementary Methods) (Sup. Fig. S2A) (18). Of 381 samples that underwent 16S sequencing, 121 fell below the KatharoSeq threshold and were excluded (Sup. Fig. 2C). Informed by alpha rarefaction curves (Sup Fig 2B), remaining samples were rarefied to 4000 features, removing an additional 36 samples from the analysis. Therefore, 157 samples were excluded from downstream analyses (122 SARS-CoV-2 negative matched swabs, 35 positive) (Sup Fig 2C).
Bacterial alpha diversity analysis demonstrated that 16S amplicon read count associated with SARS-CoV-2 detection status (Sup. Fig. S3). Forward stepwise redundancy analysis (RDA) using the unweighted UniFrac beta diversity metric identified four non-redundant variables of significant effect size (apartment, surface type, type of room, and SARS-CoV-2 detection status) which accounted for 45.4% of the variation in the data (Sup. Fig. 4B). Analyzed by apartment, only in apartment B did virus detection lack significant effect. When subsetting the entire dataset by room type, detection status had a significant effect on variability across all rooms.
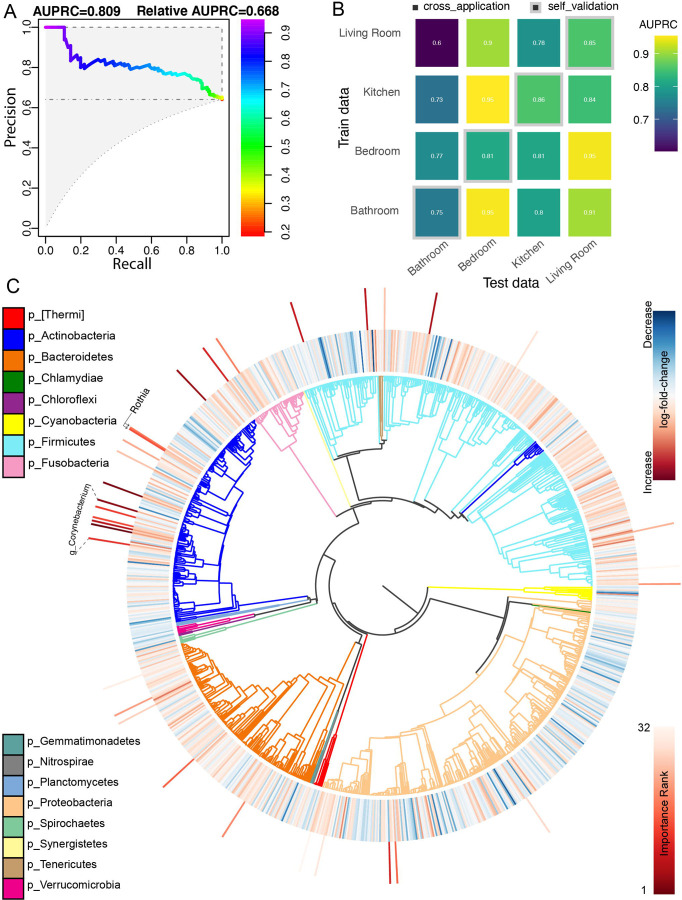
To test whether the bacterial community predicted SARS-CoV-2 status, we built a random forest classifier using sOTU data. The overall Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve (AUPRC) was 0.78, suggesting a statistically significant association, but insufficiently strong to predict SARS-CoV-2 status of a single sample from the bacterial community (Fig. 2A). Cross-application of models trained from one apartment or room type to other apartments or room types generally performed well (AUPRC=0.7–0.96), suggesting generalizable associations (Fig. 2B). We also applied multinomial regression to our dataset to identify differentially abundant microbes between SARS-CoV-2 status groups. The top 32 features identified by the random forest classifier and the ranked log-fold-changes in feature abundance from the multinomial regression are shown in Figure 2C. Agreeing with previously published findings, Rothia dentocariosa was one of the top features identified by the classifier and was relatively positively associated with SARS-CoV-2 positive samples in the regression (8,12). Six sOTUS belonging to members of the genus Corynebacterium were also highly ranked as predictive for positive samples.
Figure 2.
(A) Area under the precision-recall curve showing the overall prediction performance of the random forest classifiers when trained on the features from two apartments and cross validated on the remaining apartment. (B) Confusion matrix showing per-room type classifiers when cross-applied on the remaining room types. The diagonal represents self validation. (C) Phylogenetic tree visualization (EMPress) where the differentially-abundant features between SARS-CoV-2 status groups identified by multinomial regression (Songbird) are plotted on the inner ring, and the ranked sOTUs identified as important by the random forest classifier are indicated on the outer ring.
Discussion
Our results show that detailed spatial mapping of SARS-CoV-2 RNA abundance and associated bacterial signatures from built environment surfaces provides useful insight into potential sampling locations and associations between the viral and bacterial components of the microbiome. In the residential setting, high-touch surfaces have especially high viral loads, although confirming this with detailed spatial maps in other settings (hospitals, isolation hotels, schools) may be useful for guiding sampling designs. We note that sensitivity of arbitrary single surface sampling to detect presence of even an unmasked SARS-CoV-2 individual is low, so multiple samples or samples from selected surfaces should be collected. These results reinforce the utility of surface sampling as a cost-effective method for locating SARS-CoV-2 signals in the environment.
Our findings also corroborate SARS-CoV-2 associated changes in the microbiome published previously. Rothia dentocariosa specifically has been identified across different sample types in diverse settings, although reasons for these associations remain unclear. We also see multiple sOTUs belonging to the genus Corynebacterium predictive of a SARS-CoV-2 detection event, in contrast to the findings of another study that found Corynebacterium significantly decreased in the oral microbiome of individuals with COVID-19 (12). We hypothesize that Corynebacterium signal in this study might be evidence of human skin contamination of indoor surfaces through contact, leading to SARS-CoV-2 deposition on surfaces. It has been established that the occupants of a room contribute to the environmental microbiota, but our findings are among the first to demonstrate that disease-associated changes in the microbiome are mirrored in the built environment.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Table 1. Environmental samples with detectable SARS-CoV-2 per apartment and room type.
Supplementary Figure 1. Timeline of events from first positive test to the end of the individual’s quarantine period. Apartment C has no move in date because the individual quarantined in place.
Supplementary Figure 2. Exclusion criteria for low biomass samples. (A) Diluted stock of a KatharoSeq positive control was sequenced along with the environmental samples and the resultant reads underwent pre-processing as detailed in the Supplementary Methods.The KatharoSeq Threshold (dashed lined), a minimum number of reads derived from a fitted allosteric sigmoidal curve, corresponds to a sequencing depth where at least 80% of the positive control reads are taxonomically classified to the appropriate target organisms (B) Top panel: Rarefaction curve showing observed features (alpha diversity metric) as a function of sequencing depth. Bottom panel: Graph showing how many samples would be included in downstream analysis as a function of rarefaction depth. (C) Table showing how many samples were removed at the KatharoSeq and Rarefaction thresholds and overall.
Supplementary Figure 3. Correlation between microbial biomass/diversity and SARS-CoV-2 detection. (A) Number of 16S reads in SARS-CoV-2 positive samples shows significant correlation with SARS-CoV-2 viral load (GE’s) (Pearson correlation, r=0.3, p=3×10−5). (B) Read counts are significantly different between positive and negative samples when compared within room types (Mann-Whitney U tests, p≤0.003). (C) Alpha diversity (Faith’s PD) shows a weaker significance between positive and negative samples when compared within room types with only the bedroom and kitchen showing a significant difference between positive and negative samples (Mann-Whitney U tests, p=0.01).
Supplementary Figure 4. Beta diversity analysis identifies the factors that contribute most to the separation of the data. (A) Principal coordinates analysis of the Unweighted Unifrac distance matrix shows that a major driver in the separation of this data is which apartment the samples came from. (B) Barplot showing the statistically significant effect sizes for non-redundant variables returned by RDA analysis. The largest effect size was explained by apartment (30.7%, p=0.0002), followed by surface material type (10.7%, p=0.0002), room type (3.2%, p=0.0004), and SARS-CoV-2 detection status (0.84%, p=0.01).
Importance.
Surface sampling for detecting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is increasingly being used to locate infected individuals. We tested which indoor surfaces had high versus low viral loads by collecting 381 samples from three residential units where infected individuals resided, and interpreted the results in terms of whether SARS-CoV-2 was likely transmitted directly (e.g. touching a light switch) or indirectly (e.g. by droplets or aerosols settling). We found highest loads where the subject touched the surface directly, although enough virus was detected on indirectly contacted surfaces to make such locations useful for sampling (e.g. in schools, where students do not touch the light switches and also wear masks so they have no opportunity to touch their face and then the object). We also documented links between the bacteria present in a sample and the SARS-CoV-2 virus, consistent with earlier studies.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH grant (K01MH112436) to RFM, and the County of San Diego Health and Human Services Agency (Contract 563236). We thank Min Yi Wu, Bing Xia, Daniel Maunder, Michal Machnicki, Bhavika K. Kapadia, and Lizbeth Franco Vargas for their support with environmental SARS-CoV-2 detection as part of the EXCITE Lab.
References:
- 1.Fielding-Miller R, Karthikeyan S, Gaines T, Garfein RS, Salido R, Cantu V, Kohn L, Martin NK, Wijaya C, Flores M, Omaleki V, Majnoonian A, Gonzalez-Zuniga P, Nguyen M, Vo A V, Le T, Duong D, Hassani A, Dahl A, Tweeten S, Jepsen K, Henson B, Hakim A, Birmingham A, Mark AM, Nasamran CA, Rosenthal SB, Moshiri N, Fisch KM, Humphrey G, Farmer S, Tubb HM, Valles T, Morris J, Kang J, Khaleghi B, Young C, Akel AD, Eilert S, Eno J, Curewitz K, Laurent LC, Rosing T, SEARCH Knight R. 2021. Wastewater and surface monitoring to detect COVID-19 in elementary school settings: The Safer at School Early Alert project. medRxiv 2021.10.19.21265226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jiang FC, Jiang XL, Wang ZG, Meng ZH, Shao SF, Anderson BD, Ma MJ. 2020. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA on surfaces in quarantine rooms. Emerg Infect Dis 26:2162–2164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhou J, Otter JA, Price JR, Cimpeanu C, Meno Garcia D, Kinross J, Boshier PR, Mason S, Bolt F, Holmes AH, Barclay WS. 2021. Investigating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Surface and Air Contamination in an Acute Healthcare Setting During the Peak of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic in London. Clin Infect Dis 73:e1870–e1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ben-Shmuel A, Brosh-Nissimov T, Glinert I, Bar-David E, Sittner A, Poni R, Cohen R, Achdout H, Tamir H, Yahalom-Ronen Y, Politi B, Melamed S, Vitner E, Cherry L, Israeli O, Beth-Din A, Paran N, Israely T, Yitzhaki S, Levy H, Weiss S. 2020. Detection and infectivity potential of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) environmental contamination in isolation units and quarantine facilities. Clin Microbiol Infect 26:1658–1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Renninger N, Nastasi N, Bope A, Cochran SJ, Haines SR, Balasubrahmaniam N, Stuart K, Bivins A, Bibby K, Hull NM, Dannemiller KC. 2021. Indoor Dust as a Matrix for Surveillance of COVID-19. mSystems 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maestre JP, Jarma D, Yu JRF, Siegel JA, Horner SD, Kinney KA. 2021. Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 RNA signal in a home with COVID-19 positive occupants. Sci Total Environ 778:146201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu S, Wang Y, Jin X, Tian J, Liu J, Mao Y. 2020. Environmental contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in a designated hospital for coronavirus disease 2019. Am J Infect Control 48:910–914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marotz C, Belda-Ferre P, Ali F, Das P, Huang S, Cantrell K, Jiang L, Martino C, Diner RE, Rahman G, McDonald D, Armstrong G, Kodera S, Donato S, Ecklu-Mensah G, Gottel N, Salas Garcia MC, Chiang LY, Salido RA, Shaffer JP, Bryant MK, Sanders K, Humphrey G, Ackermann G, Haiminen N, Beck KL, Kim H-C, Carrieri AP, Parida L, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Torriani FJ, Knight R, Gilbert J, Sweeney DA, Allard SM. 2021. SARS-CoV-2 detection status associates with bacterial community composition in patients and the hospital environment. Microbiome 9:132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dunn RR, Fierer N, Henley JB, Leff JW, Menninger HL. 2013. Home Life: Factors Structuring the Bacterial Diversity Found within and between Homes. PLoS One 8:e64133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kembel SW, Jones E, Kline J, Northcutt D, Stenson J, Womack AM, Bohannan BJ, Brown GZ, Green JL. 2012. Architectural design influences the diversity and structure of the built environment microbiome. ISME J 6:1469–1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lax S, Smith DP, Hampton-Marcell J, Owens SM, Handley KM, Scott NM, Gibbons SM, Larsen P, Shogan BD, Weiss S, Metcalf JL, Ursell LK, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Van Treuren W, Hasan NA, Gibson MK, Colwell R, Dantas G, Knight R, Gilbert JA. 2014. Longitudinal analysis of microbial interaction between humans and the indoor environment. Science (80-) 345:1048–1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wu Y, Cheng X, Jiang G, Tang H, Ming S, Tang L, Lu J, Guo C, Shan H, Huang X. 2021. Altered oral and gut microbiota and its association with SARS-CoV-2 viral load in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 7:61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gu S, Chen Y, Wu Z, Chen Y, Gao H, Lv L, Guo F, Zhang X, Luo R, Huang C, Lu H, Zheng B, Zhang J, Yan R, Zhang H, Jiang H, Xu Q, Guo J, Gong Y, Tang L, Li L. 2020. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza. Clin Infect Dis 71:2669–2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amir A, McDonald D, Navas-Molina JA, Kopylova E, Morton JT, Zech Xu Z, Kightley EP, Thompson LR, Hyde ER, Gonzalez A, Knight R. 2017. Deblur Rapidly Resolves Single-Nucleotide Community Sequence Patterns. mSystems 2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gonzalez A, Navas-Molina JA, Kosciolek T, McDonald D, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Ackermann G, DeReus J, Janssen S, Swafford AD, Orchanian SB, Sanders JG, Shorenstein J, Holste H, Petrus S, Robbins-Pianka A, Brislawn CJ, Wang M, Rideout JR, Bolyen E, Dillon M, Caporaso JG, Dorrestein PC, Knight R. 2018. Qiita: rapid, web-enabled microbiome meta-analysis. Nat Methods 15:796–798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodríguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Bin Kang K, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu Y-X, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik A V., Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG. 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Salido RA, Cantú VJ, Clark AE, Leibel SL, Foroughishafiei A, Saha A, Hakim A, Nouri A, Lastrella AL, Castro-Martínez A, Plascencia A, Kapadia BK, Xia B, Ruiz CA, Marotz CA, Maunder D, Lawrence ES, Smoot EW, Eisner E, Crescini ES, Kohn L, Vargas LF, Chacón M, Betty M, Machnicki M, Wu MY, Baer NA, Belda-Ferre P, De Hoff P, Seaver P, Ostrander RT, Tsai R, Sathe S, Aigner S, Morgan SC, Ngo TT, Barber T, Cheung W, Carlin AF, Yeo GW, Laurent LC, Fielding-Miller R, Knight R. 2021. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Persistence across Indoor Surface Materials Reveals Best Practices for Environmental Monitoring Programs. mSystems 10.1128/MSYSTEMS.01136-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Minich JJ, Zhu Q, Janssen S, Hendrickson R, Amir A, Vetter R, Hyde J, Doty MM, Stillwell K, Benardini J, Kim JH, Allen EE, Venkateswaran K, Knight R. 2018. KatharoSeq Enables High-Throughput Microbiome Analysis from Low-Biomass Samples. mSystems 3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Morton JT, Marotz C, Washburne A, Silverman J, Zaramela LS, Edlund A, Zengler K, Knight R. 2019. Establishing microbial composition measurement standards with reference frames. Nat Commun 10:2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cantrell K, Fedarko MW, Rahman G, McDonald D, Yang Y, Zaw T, Gonzalez A, Janssen S, Estaki M, Haiminen N, Beck KL, Zhu Q, Sayyari E, Morton JT, Armstrong G, Tripathi A, Gauglitz JM, Marotz C, Matteson NL, Martino C, Sanders JG, Carrieri AP, Song SJ, Swafford AD, Dorrestein PC, Andersen KG, Parida L, Kim H-C, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Knight R. 2021. EMPress Enables Tree-Guided, Interactive, and Exploratory Analyses of Multi-omic Data Sets. mSystems 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Protsyuk I, Melnik A V., Nothias LF, Rappez L, Phapale P, Aksenov AA, Bouslimani, Ryazanov S, Dorrestein PC, Alexandrov T. 2017. 3D molecular cartography using LC–MS facilitated by Optimus and ‘ili software. Nat Protoc 2017 131 13:134–154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hunter J. D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 9, 90–95 (2007). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 1. Environmental samples with detectable SARS-CoV-2 per apartment and room type.
Supplementary Figure 1. Timeline of events from first positive test to the end of the individual’s quarantine period. Apartment C has no move in date because the individual quarantined in place.
Supplementary Figure 2. Exclusion criteria for low biomass samples. (A) Diluted stock of a KatharoSeq positive control was sequenced along with the environmental samples and the resultant reads underwent pre-processing as detailed in the Supplementary Methods.The KatharoSeq Threshold (dashed lined), a minimum number of reads derived from a fitted allosteric sigmoidal curve, corresponds to a sequencing depth where at least 80% of the positive control reads are taxonomically classified to the appropriate target organisms (B) Top panel: Rarefaction curve showing observed features (alpha diversity metric) as a function of sequencing depth. Bottom panel: Graph showing how many samples would be included in downstream analysis as a function of rarefaction depth. (C) Table showing how many samples were removed at the KatharoSeq and Rarefaction thresholds and overall.
Supplementary Figure 3. Correlation between microbial biomass/diversity and SARS-CoV-2 detection. (A) Number of 16S reads in SARS-CoV-2 positive samples shows significant correlation with SARS-CoV-2 viral load (GE’s) (Pearson correlation, r=0.3, p=3×10−5). (B) Read counts are significantly different between positive and negative samples when compared within room types (Mann-Whitney U tests, p≤0.003). (C) Alpha diversity (Faith’s PD) shows a weaker significance between positive and negative samples when compared within room types with only the bedroom and kitchen showing a significant difference between positive and negative samples (Mann-Whitney U tests, p=0.01).
Supplementary Figure 4. Beta diversity analysis identifies the factors that contribute most to the separation of the data. (A) Principal coordinates analysis of the Unweighted Unifrac distance matrix shows that a major driver in the separation of this data is which apartment the samples came from. (B) Barplot showing the statistically significant effect sizes for non-redundant variables returned by RDA analysis. The largest effect size was explained by apartment (30.7%, p=0.0002), followed by surface material type (10.7%, p=0.0002), room type (3.2%, p=0.0004), and SARS-CoV-2 detection status (0.84%, p=0.01).