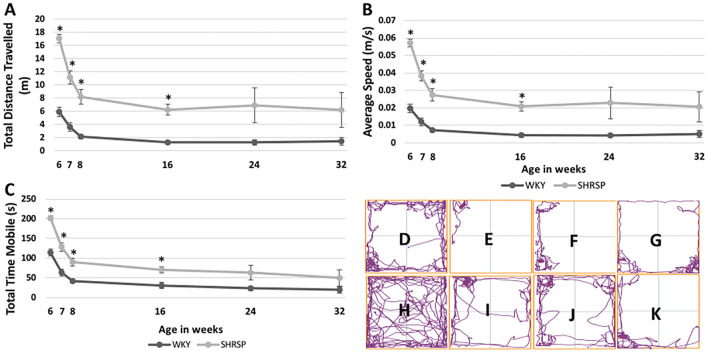
Figure 2.
Temporal changes of sensorimotor testing in WKY and SHRSP presented at 6, 7, 8, 16, 24, and 32 weeks of age. Compared to WKY, SHRSP were found to have motor restlessness as represented by a longer total distance traveled during the testing period (A), higher average speed (B) and longer total mobile time (C). The differences between SHRSP and WKY, were statistically significant at 6, 7, 8, and 16 weeks of age while they became not statistically different afterwards. Head tracing of one WKY at [6 (D), 16 (E), 24 (F), and 32 (G) weeks of age] and one SHRSP at the same time points [6 (H), 16 (I), 24 (J), and 32 (K)] weeks of age is shown which visually demonstrates larger decrease in activity during the experiment in SHRSP compared to WKY. WKY, Wistar Kyoto Rats; SHRSP, Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats; m: meter; s, second, m/s, meter per second; *, statistically significant difference of P < 0.05.