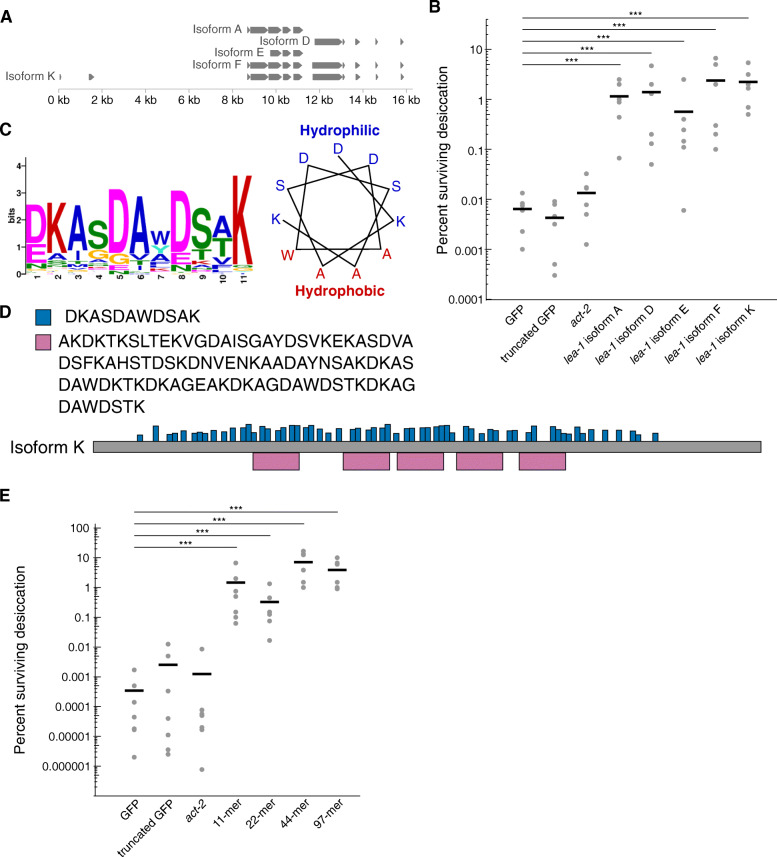
Fig. 7.
Heterologous expression of C. elegans lea-1 isoforms and motifs improves bacterial desiccation survival. A Select isoforms of LEA-1 used for bacterial expression. B Desiccation survival of BL21 E. coli expressing codon-optimized C. elegans LEA-1 isoforms. Heterologous expression of each isoform increased desiccation survival (1-way ANOVA p < 0.0001, post-hoc Dunnett’s test: Isoform A p < 0.0001, Isoform D p < 0.0001, Isoform E p = 0.0008, Isoform F p < 0.0001, Isoform K p < 0.0001, each isoform compared to GFP control, n = 6). C A consensus 11-mer motif found in LEA-1 likely forms an amphipathic alpha helix. The position weight matrix of amino acids in the motif is shown, as well as a wheel diagram depicting the relative position of each consensus amino acid in an alpha helical conformation. D Consensus amino acid sequences are shown for the 11-mer as well as a 97-mer motif that was also detected with an expanded motif window size. The frequency and distribution of occurrences of these motifs within isoform K are shown. E Desiccation survival of BL21 E. coli is significantly increased by expression of motifs of LEA-1. Codon-optimized sequences for the 11-mer, as well as concatenated repeats of the 11-mer sequence (2x = 22-mer, 4x = 44-mer), and the 97-mer motif were expressed. Expression of each peptide increased survival of desiccated bacteria (1-way ANOVA p < 0.0001, post-hoc Dunnett’s test: 11-mer p < 0.0001, 22-mer p < 0.0001, 44-mer p < 0.0001, 97-mer p < 0.0001, compared to GFP control, n = 7). ***p < 0.001