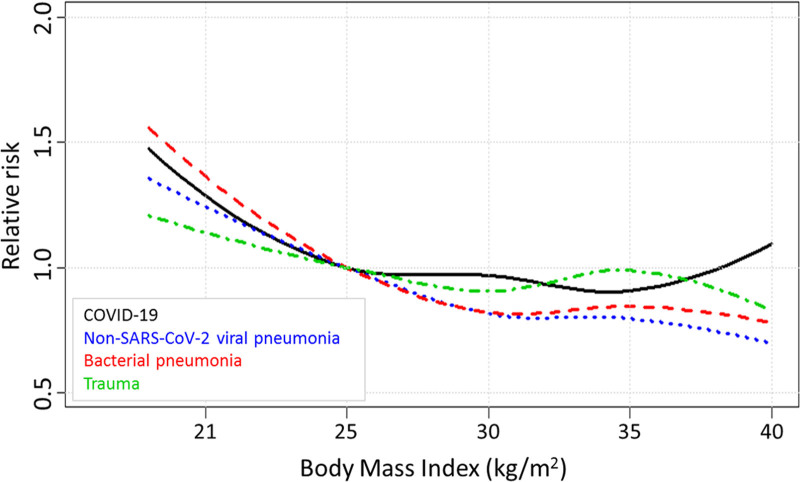
Figure 2.
Relative inhospital mortality risks according to body mass index (BMI) in the four cohorts. BMI of 25.0 kg/m2 was used as reference. Relative risks were adjusted for sex, age, chronic diagnosis, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III Acute Physiology Score and need for mechanical ventilation, use of vasoactive medication, and lowest Pao2/Fio2 ratio in the first 24 hr following ICU admission. The mortality risk decreases with higher BMI in the nonsevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, and trauma cohorts, but not in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.