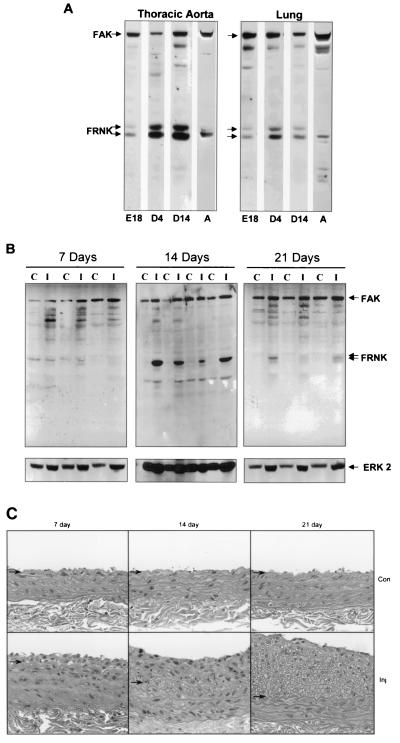
FIG. 2.
Expression of FRNK in smooth muscle tissues during development and following vascular injury. (A) Thoracic aorta and lung tissues were dissected from animals during development. Protein extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western immunoblot analysis as described in the legend to Fig. 1. E, embryonic day; D, day after birth; A, adult. Tissues were pooled from four rat embryos and two neonates (day 4). Data are representative of three separate experiments. (B) Rat carotid arteries were injured by balloon-mediated endothelial denudation. Vessels were dissected either 7, 14, or 21 days postinjury from the injured left carotid (I) or control contralateral right carotid (C) artery. Extracts were prepared, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with anti-FAK carboxyl-terminal Ab (top) or anti-extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 2 to serve as a loading control (bottom). No significant differences in FAK pTyr were observed as determined by blotting with a phosphorylation-specific Ab to Y397 of FAK (data not shown). Data are representative of seven animals per time point from two separate experiments. (C) Histological staining of uninjured control (Con) or injured (Inj) sections 7, 14, or 21 days following surgery. Arrows denote the position of the internal elastic lamina.