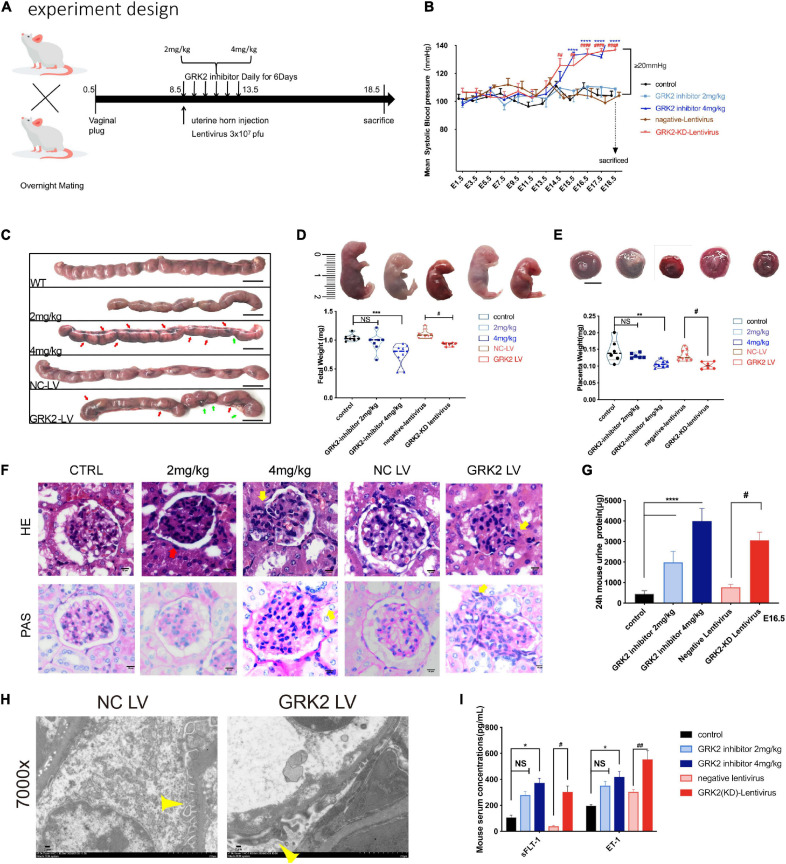
FIGURE 2.
Knockdown or inhibition of GRK2 in placenta induces PE-like phenotype:hypertension, proteinuria, and angiogenic imbalance in mice. (A) Experimental design. For each group, n = 6–10 mice. (B) Blood pressure was taken in mice with/without placental knockdown or inhibition of GRK2. n > 6, Mean ± SEM. (C) Gross morphology of uterus at E18.5 shows the spontaneous hemorrhage and resorptions of embryos in uteri of GRK2 deficient groups. Green arrows, fetal resorption; red arrows, intrauterine hemorrhage. (D,E) Knockdown or inhibition of placental GRK2 induced embryo growth restriction and placenta growth restriction. (F,G) Glomerular histopathology assessment by HE (upper panel) and PAS (lower panel) staining of untreated mice and mice treated with GSK180736A (2 or 4 mg/kg), and mice receiving intrauterine injections with non-target/GRK2-knockdown lentivirus. Scale bar, 10 μm. Mesangial hyperplasia (yellow arrow) and decreased capillary density (red arrow) are shown in GRK2-knockdown/inhibition group. (H) TEM analysis of glomerulus. Pathological podocyte fusion in GRK2-knockdown group and the podocytes in NC-LV group are indicated by thin yellow arrows; 7,000× magnification, Scale bar, 2 μm. (I) the sFlt1 and ET-1 abundance in serum of E18.5 mice, as determined by ELISA. sFlt1, soluble fms-related tyrosine kinase-1; ET-1, Endothelin-1. All data are represented as X ± SEM from each experiment (n = 6–10 mice, each assayed individually), NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus control mice group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 versus NC-LV mice group.