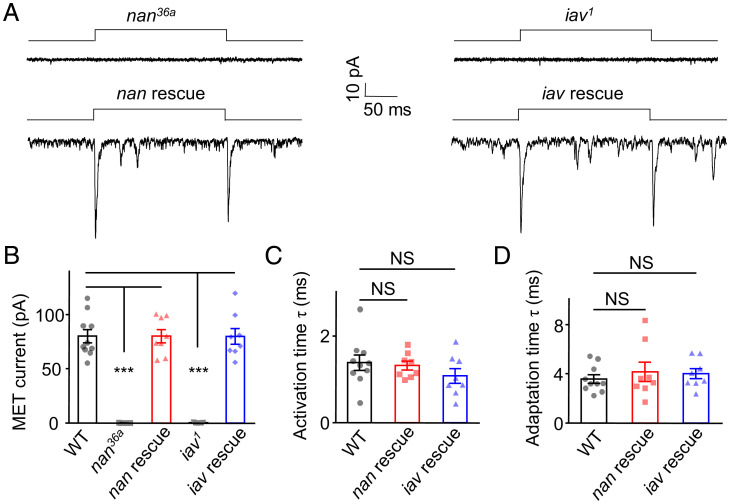
Fig. 3.
NAN and IAV are required for mechanical stimuli–induced whole-cell current in lch1 Cho neurons. (A) Current response to a mechanical stimulus (1 μm) was eliminated in nan and iav null mutants but could be rescued by expressing NAN and IAV in lch1 neurons of nan36a and iav1 mutants, respectively. Lch1 neurons were clamped at −60 mV (holding potential) in Na+/K+-based solutions. (B) Bar graph summarizing the peak current (absolute value) of the lch1 neurons in wild-type (WT), nan36a, nan rescue, iav1, and iav rescue larvae (n = 10, 7, 8, 9, and 8, respectively; mean ± SEM). (C) The activation time constants of MET currents in larvae with indicated genotype (n = 10, 8, 8, respectively, mean ± SEM). (D) Summary of the adaptation time constants of MET currents in WT, nan rescue, and iav rescue larvae (n = 10, 8, and 8, respectively; mean ± SEM). The unpaired t test was used for comparison between two groups, and one-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Šidák post hoc analysis was used for comparison among multiple groups. ***P < 0.001. NS, not statistically significant. Genotypes are as follows: nan36a: Iav-Gal4/UAS-GFP; nan36a/nan36a. iav1: iav1/y; Iav-Gal4/+; UAS-CD8-GFP/+. nan rescue: Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/UAS-Nanchung-GFP; nan36a/nan36a. iav rescue: iav1/y; Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/+; UAS-Inactive-GFP/+. WT: Iav-Gal4/+; UAS-CD8-GFP/+.